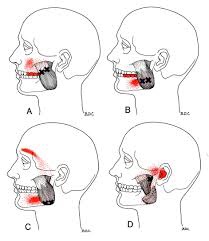
First, what is whiplash? It’s a lot of things, which is why the term WAD or Whiplash Associated Disorders has become the most common term for the main signs and symptoms associated with a whiplash injury. WAD is usually associated with a motor vehicle collision, but sports injuries, diving accidents, and falls are other common ways to sustain a WAD injury.
To answer the question of the month, in most cases, the recovery rate is high and favors those who resume their normal daily activities. The worse thing you can do when you sustain a WAD injury is to not do anything! Too much rest and inactivity leads to long-term disability. Of course, this must be balanced with the degree of injury, but even when the injury requires some “down time,” stay as active as possible during the healing phase.
Many people recover within a few days or weeks while a smaller percentage require months and about 10% may only partially recover. So what can be done to give you the best possible chance to fully recover as soon as possible?
During recovery, you can expect your condition to fluctuate in intensity so “listen” to your body, let it “guide” you during activity and exercise, and stay within “a reasonable boundary of pain” during your activity. Remember, your best chance for full recovery FAVORS continuing a normal lifestyle. Make reasonable modifications so you can work, socialize, and do your “normal” activities!
The KEY: Stay in control of your condition – DO NOT let it control you! Here are some tips:
1) POSTURE CONTROL: Keep the weight of the head back by gliding your chin back until you “hit” a firm end-point. Then release it slightly so it’s comfortable—this is your NEW head position!
2) FLEXIBILITY: Try this range of motion (ROM) exercise… Slowly flex your neck forwards and then backwards, then bend your neck to the left and then the right, and then rotate it to the left and to then to the right. THINK about each motion and avoid sharp, knife-like pain; a “good-hurt” is okay! Next, do the same thing with light (one-finger) resistance in BOTH directions. Try three slow reps four to six times a day!
3) MUSCLE STRENGTH: Try pushing your head gently into your hand in the six directions listed above to provide a little resistance. Next, reach back with both hands or wrap a towel around your neck and pull forwards on the towel while you push the middle of your neck backwards into the towel doing the chin-tuck/glide maneuver (same as #1). Repeat three to five times slowly pushing, and more importantly, release the push slower! This is the MOST IMPORTANT of the strengthening exercises in most cases! Next, “squeeze” your shoulder blades together followed by spreading them as far apart as possible (repeat three to five times).
4) PERIODIC BREAKS: Set a timer to remind yourself to do a stretch, get up and move, to tuck your chin inwards (#1) and do some of #2 and #3 every 30-60 minutes.
5) LIFTING/CARRYING/WORK: Be SMART! Do not re-injure yourself. Change the way you handle yourself in your job, in the house, and while performing recreational activities.
6) HOUSEHOLD ACTIVITIES: Use a dolly to move boxes and keep commonly used items within easy reach (not too high or low).