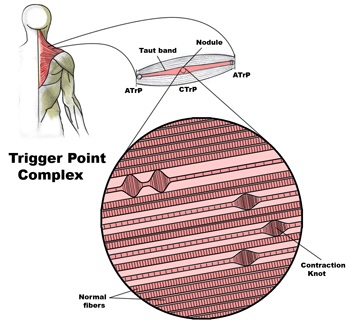
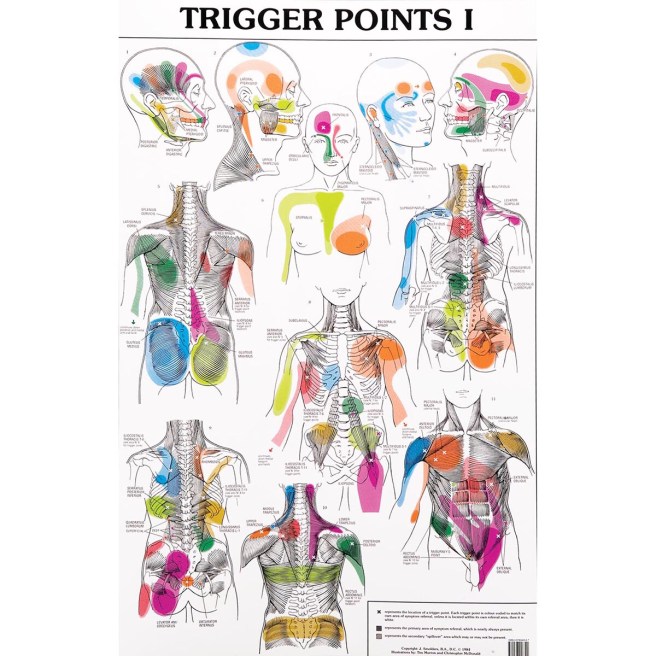
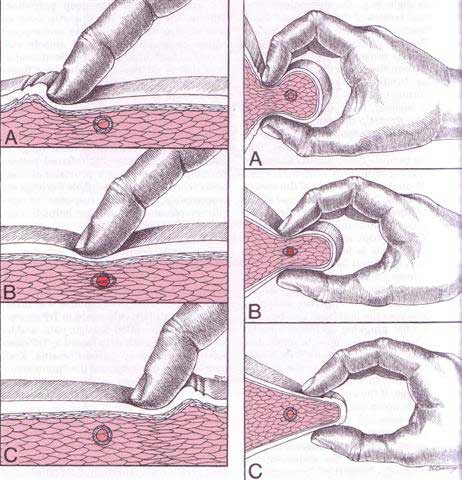
Chiropractic is the most widely accepted and most frequently used type of “alternative” healthcare in the United States. This is largely due to the fact that it works, and because of that, there has been a steady increase in acceptance by the public, third-party payers, and the Federal government. Since the mid-1990s, a number of outside (non-chiropractic) observers have suggested that chiropractic has now entered mainstream healthcare.
One can position chiropractic as being BOTH alternative and mainstream. It is “alternative” since it approaches healthcare from an entirely different direction compared to the primary care medical profession. Chiropractic is non-surgical and promotes diet and nutritional approaches vs. drugs and surgery. Chiropractic is also arguably “mainstream” as it has evolved into a strongly utilized form of primary care through popular acceptance and utilization by the public.
So, what role does chiropractic play in today’s health delivery system? This question is still being debated, but there appears to be three camps: 1) Specialist—limited to musculoskeletal (MSK) complaints on an interdisciplinary primary healthcare team; 2) Primary healthcare “gatekeepers” that focus on ambulatory MSK complaints; 3) Generalist primary healthcare provider of “alternative or complementary” medicine that manage and/or co-manage both MSK AND non-MSK conditions.
Looking at this from the patient or “consumer” perspective, chiropractic already plays an important role in the healthcare delivery for many patients. In 1993, a report claimed 7% of American adults had received chiropractic care during the prior year. According to a 2015 Gallup poll (that included 5,442 adults, aged 18+, surveyed between 2/16/15 and 5/6/15) entitled, Majority in U.S. Say Chiropractic Works for Neck, Back Pain, “Chiropractic care has a positive reputation among many US adults for effective treatment of neck and back pain, with about six in 10 adults either strongly agreeing (23%) or agreeing somewhat (38%) that chiropractors are effective at treating these types of pain.”
The “highlights” from this Gallup poll include: 1) Two-thirds say chiropractic is effective for neck and back pain. 2) Many adults say chiropractors think of the patient’s best interest. 3) More than 33 million adults in the United States (US) saw a chiropractor in the twelve months before the survey was conducted. That means roughly 14% of U.S. adults saw a chiropractor in the 12 months prior to the survey (vs. 7% in 1993). An additional 12% who responded to the Gallup pollsters saw a chiropractor in the last five years but not in the last 12 months. Overall, 51% of those polled had previously seen a chiropractor.
Whether or not you have personally utilized chiropractic, the educational process, licensing requirements, public interest, third-party payer systems, and interprofessional cooperation ALL support firm ground for which you can comfortably and confidently seek chiropractic care for your complaints.
We realize you have a choice in whom you consider for your health care provision and we sincerely appreciate your trust in choosing our service for those needs. If you, a friend, or family member requires care, we would be honored to render our services.