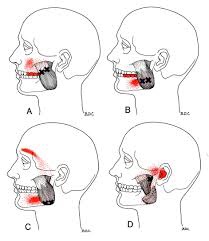
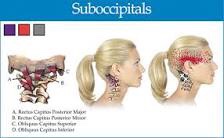
Whiplash, or better termed “Whiplash Associated Disorders” (WAD), is a condition that carries multiple signs and symptoms ranging from neck pain and stiffness to headache, confusion, ringing in the ears, and more. But can WAD cause dizziness? Let’s take a look!
Dizziness is a general term that is used rather loosely by the general population. We’ve all experienced dizziness from time-to-time that is considered “normal,” such as standing up too quickly or while experiencing a rough flight.
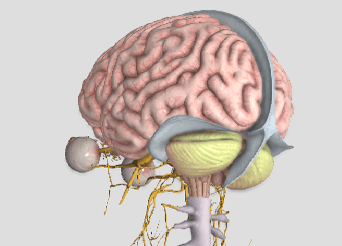
Often, dizziness and problems with balance go hand in hand. There are three main organs that control our balance: 1) the vestibular system (the inner ear); 2) the cerebellum (lies in the back of the head); and, 3) the dorsal columns (located in the back part of the spinal cord). In this article, we will primarily focus on the inner ear because, of the three, it’s unique for causing dizziness. Our vision also plays an important role in maintaining balance, as we tend to lose our balance much faster when we close our eyes.
It’s appropriate to first discuss the transient, usually short episode of “normal” lightheadedness associated with rising quickly. This is typically caused by a momentary drop in blood pressure, and hence, oxygen simply doesn’t reach the brain quick enough when moving from sitting to standing. Again, this is normal and termed “orthostatic hypotension” (OH).
However, OH can be exaggerated by colds, the flu, allergy flair-ups, when hyperventilating, or at times of increased stress or anxiety. OH is also associated with the use of tobacco, alcohol, and/or some medications. Bleeding can represent a more serious cause of OH such as with bleeding ulcers or some types of colitis, and less seriously, with menstruation.
The term BPPV or benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, has to do with the inner ear where our semicircular canals are located. The canals lie in three planes and give us a 3D, 360º perspective about where we are in space. The fluid flowing through these canals bends little hair-like projections, which are connected to sensory nerves that tell the brain about our spatial position. If the function of these canals is disturbed, it can mix-up the messages the brain receives, thus resulting in dizziness. Exercises are available on the Internet that can help with BPPV (look for Epley’s and Brandt-Daroff exercises).
DANGEROUS causes of dizziness include: HEART – fainting (passing out) accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, pain or pressure in the back, neck, jaw, upper belly, or in one or both arms, sudden weakness, and/or a fast or irregular heartbeat.
STROKE – sudden numbness, paralysis, or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially if only on one side of the body; drooling, slurred speech, short “black outs,” sudden visual changes, confusion/difficulty speaking, and/or a sudden and severe, “out of the ordinary” headache. CALL 911 (or the number for emergency services if you’re outside the Canada) if you suspect you may be having a heart attack or stroke!