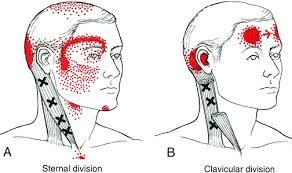
The medial pteragoyd muscle is located on the inside of the jaw. It is responsible for jaw movements during talking and chewing. This muscle becomes over loaded from poor neck posture as well as stress resulting in grinding the teeth or excessive clenching of the jaw. Trigger points in this muscle will refer deep into the jaw and the tempomandibular joint producing “tmj dysfunction syndrome.