Your spine consists of 24 individual vertebrae stacked on top of each other. Flexible cushions called “discs” live between each set of vertebrae. A disc is made up of two basic components. The inner disc, called the “nucleus”, is like a ball of jelly about the size of a marble. This jelly is held in place by the outer part of the disc called the “annulus”, which is wrapped around the inner nucleus much like a ribbon wrapping around your finger. The term lumbar disc lesion means that your disc has been damaged.


Disc lesions start when the outer fibers of the disc become strained or frayed. If enough fibers become frayed, this can create a weakness and when the disc is compressed, the outer fibers may “bulge” or “protrude” like a weak spot on an inner tube. If more fibers are damaged, the nucleus of the disc may “herniate” outward. Since the spinal cord and nerve roots live directly behind the disc, bulges that are accompanied by inflammation will likely create lower back pain that radiates into the buttock or the entire lower extremity. This condition is called sciatica. If the disc bulge is significant enough to create a mechanical compression of your nerve, you may also experience loss of your reflexes and weakness. Be sure to let our office know if you notice progressive weakness or numbness, any numbness around your groin, any loss of bowel or bladder control or fever.
Surprisingly, disc bulges are present without any symptoms in about 1/3 of the adult population. Another one third of adults will experience pain from a lumbar disc at some point in their lifetime. The condition is more common in men. Most lumbar disc problems occur at one of the two lowest discs- L5 or L4. Smokers and people who are generally inactive have a higher risk of lumbar disc problems. Certain occupations may place you at a greater risk, especially if you spend extended periods of time sitting or driving. People who are tall or overweight have increased risk of disc problems. The condition is uncommon in children and is most common between the ages of 40 and 60.
Researches have shown that disc bulges and sciatica may be successfully managed with conservative care like the type we will provide.


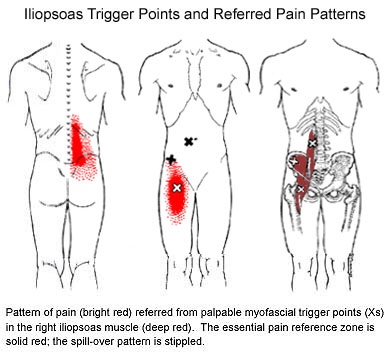
 Your lower back is made up of 5 bones stacked on top of each other with a soft “disc” between each segment to allow for flexibility. Normally, each joint in your spine should move freely and independently. Our examination of your spine has shown that one or more of the joints in your low back is slightly misaligned and restricted. We call this condition “lumbar segmental joint restriction”.
Your lower back is made up of 5 bones stacked on top of each other with a soft “disc” between each segment to allow for flexibility. Normally, each joint in your spine should move freely and independently. Our examination of your spine has shown that one or more of the joints in your low back is slightly misaligned and restricted. We call this condition “lumbar segmental joint restriction”.