These muscles are located in the groin. The longus originates on the pubic body just below the pubic crest and inserts on the middle third of the linea aspera.The brevis muscle originates on the inferior ramus and body of the pubis and has its attachment to the lesser trochanter and linea aspera of the femur. Trigger points in these muscles are the most common muscular cause of groin pain. Distal trigger points refer pain to the upper medial knee and down the tibia. Proximal trigger points refer into the anterior hip area.
workout
Bryan Cobb RMT.
Since 2005, Bryan has been dedicated to helping all people with chronic and acute pain caused by soft-tissue damage.
His training and experience make him uniquely qualified to treat a wide variety of pain and dysfunction and to give instruction on prevention and self-care.
Bryan is the only Massage Therapist in Manitoba — and one of the few in Canada — to be certified by the Certification Board for Myofascial Trigger Point Therapists (CBMTPT).
Bryan holds a degree as an Advanced Remedial Massage Therapist (ARMT) from the Massage Therapy College of Manitoba. Course work at MTCM includes
• over 2,000 hours of practice, as well as
• intensive course work,
• a supervised clinical practicum, and
• community outreach placements.MTCM has a credit transfer affiliation with the University of Winnipeg, ensuring that its courses are held to the highest level. When Bryan studied at MTCM, the college was the only massage therapy college in western Canada accredited by the Commission on Massage Therapy Accreditation. Today, the college is a member of the Canadian Council of Massage Therapy Schools.
Bryan is a member in good standing of the Natural Health Practitioners of Canada.
Bryan also has a background in Anatomy, Exercise Physiology, and Sport Sciences from the University of Manitoba, and he has worked as a personal trainer and fitness leader.
He is an avid natural bodybuilder and fitness enthusiast, and has a blue belt in Brazilian jiu-jitsu.
Trigger points in the Quadratus Lumborum muscle.
The quadratus lumborum muscle is a commonly overlooked source of low back pain and is often responsible for “pseudo disc syndrome”. This muscle originates on the inferior border of the 12th rib and lumbar transverse processes. It inserts on the iliac crest and iliolumbar ligament. The q.l.’s main actions are extension and lateral flexion of the spine. It also acts as a stabilizer of the lumbar spine. Trigger points in this muscle refer pain into the sacroiliac joint and the lower buttock. Pain can also spread anteriorly along the crest of the ilium into the lower abdomen and groin and to the greater trochanter. 
What is a knee sprain?
“Ligaments” are made up of many individual fibers running parallel to each other and bundled to form a strong fibrous band. These fibrous bands hold your bones together. Just like a rope, when a ligament is stretched too far, it begins to fray or tear. “Sprain” is the term used to describe this tearing of ligament fibers.


Sprains are graded by the amount of damage to the ligament fibers. A Grade I sprain means the ligament has been painfully stretched, but no fibers have been torn. A Grade II sprain means some, but not all of the ligamentous fibers, have been torn. A Grade III sprain means that all of the ligamentous fibers have been torn, and the ligament no longer has the ability to protect the joint. Knee sprains commonly involve one or more of your knee’s ligaments including: the medial collateral, lateral collateral, anterior cruciate, and posterior cruciate.
Most knee sprains begin as the result of a sudden stop, twist, or blow from the side or front. Some patients recall a “pop” or “snap” at the time of injury. Knee sprains cause pain and swelling within the joint. Your knee may be tender to touch, and some patients report a sensation of “giving way” or difficulty walking.
Most knee sprains can be successfully managed without surgery but will require some work on your part. Initially, a period of rest may be necessary in order to help you heal. Mild Grade I sprains may return to activity in a couple of days, while more severe injuries may take six weeks or longer to recover. You can help reduce swelling by elevating your knee and using an ACE wrap for compression. Applying ice or ice massage for 10 minutes each hour may help relieve swelling. Depending upon the severity of your sprain, you may need to wear a knee brace to help protect you from further injury. If walking is painful, crutches may be necessary.
I’ve got Shin Splints; what do I do?
Shin splints, also called “Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome,” (MTSS) is caused when the muscles of your lower leg pull too hard on your bone, causing local pain and inflammation. Over half of all leg pain in athletes is caused from shin splints. Up to 1/3 of runners and soldiers experience shin splints at some point in their lifetime.
MTSS is an overuse injury frequently seen in sports involving running, jumping, or frequent stopping & starting, i.e. field hockey, soccer and cross-country. Shin splints do not occur overnight but over a period of time, often show up during the first two or three weeks of training for a new season. Shin splints can occur when there are changes to your exercise regimen, such as an increase in activity, change in shoes or a change in the surface you play on. Some doctors refer to these training areas as “the terrible toos,” – too much, too hard, too long, too fast.

Symptoms of shin splints include tenderness or pain over the inside lower portion of your shin. The discomfort begins at the start of exercise and eases as you continue. Some patients report “bumps” when touching the inner portion of their leg bone. Be sure to tell your doctor if you experience weakness, numbness or cold feet during exercise or find a very small area of sensitivity.
Unfortunately, MTSS usually develops during a time when you are training heavily for a sport or an upcoming event. Continuing this activity will often lead to ongoing problems and decreased performance. Shin splints are now believed to be a forerunner to stress fracture, so adequate rest is critical. You may need to consider non-weight bearing cross training, such as using a stationary cycle or pool running.
When directed, your return to activity should start slowly, beginning with a 1/4 mile run and progressing by 1/4 mile each time you have no pain for two consecutive workouts. You should initially avoid running on hard or uneven surfaces and begin at a lower intensity and distance, increasing by no more than 10-15% per week- first increase distance, then pace, and avoid hard or unlevel surfaces, including hills.
Sports creams and home ice massage may provide some relief. Use ice after any activity. Patients who have flat feet are predisposed to developing shin splints and may need arch supports or orthotics. Avoid using heel cushions in your shoes, as they may increase the recurrence of this problem.
Trigger points in the serratus anterior
The serratus anterior muscle is located along the sides of the ribs. It originates on the outer surface of the upper 8-9ribs, and inserts on the medial border of the scapula. This muscle acts on the scapula in several different ways. First it rotates the scapula to turn the glenoid fossa upward. It also protracted and elevates the scapula. And lastly it helps to prevent wining. This muscle is often shortened from prolonged sitting and work on a computer. Active trigger points in this muscle refer pain locally around the trigger point with spillover down the inside of the arm. Pain can also radiate into the inferior angle of the scapula. 
Trigger points in the iliopsoas muscle
This muscle originates on the bodies and disks of T12-L5 and the inner ilium. It inserts on the lesser trochanter of the femur. The psoas flexes the hip when the spine is fixed. When the leg is fixed it extends the lumbar spine increasing lumbar lordosis. This Muscle is often chronically shortened due to inactivity and sitting posture. When trigger points are present they will refer pain primarily to the lower lumbar area and the sacrum as well as into the anterior thigh. Trigger points in the iliopsoas muscle can mimic appendicitis.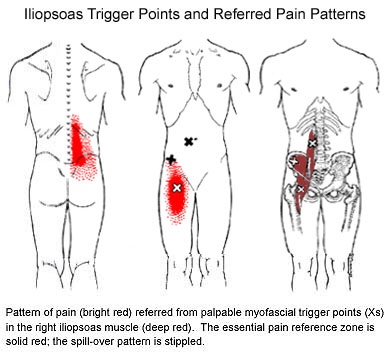
My abductors are weak, what does that mean?

Weakness of the gluteus medius allows your pelvis to drop and your knee to dive inward when you walk or run. This places tremendous strain on your hip and knee and may cause other problems too. When your knee dives inward, your kneecap is forced outward, causing it to rub harder against your thigh bone- creating a painful irritation and eventually arthritis. Walking and running with a relative “knock knee” position places tremendous stress on the ligaments around your knee and is a known cause of “sprains”. Downstream, a “knock knee” position puts additional stress on the arch of your foot, leading to other painful problems, like plantar fasciitis. Upstream, weak hips allow your pelvis to roll forward which forces your spine into a “sway back” posture. This is a known cause of lower back pain. Hip muscle weakness seems to be more common in females, especially athletes.
You should avoid activities that cause prolonged stretching of the hip abductors, like “hanging on one hip” while standing, sitting crossed legged, and sleeping in a side-lying position with your top knee flexed and touching the bed. Patients with fallen arches may benefit from arch supports or orthotics. Obesity causes more stress to the hip muscles, so overweight patients may benefit from a diet and exercise program. The most important treatment for hip abductor weakness is strength training. Hip strengthening is directly linked to symptom improvement. Moreover, people with stronger hip muscles are less likely to become injured in the first place. The exercises listed below are critical for your recovery.
Meet the Hip Cycle. You can thank me later.
1. Side lying with back and shoulders against a wall so you can’t roll back.
2. Bend your bottom leg and put the sole of your foot against the wall to be more stable.
3. Start position is with your foot directly in line with your hip. Do not let it get any lower than that. The highest point of your foot needs to be the bump on the outside of your ankle.
Do 5-10 reps of each of the following without rest between exercises twice a day. The goal is 20 reps each.
a. 6″ leg raises in abduction
b. Knee up to chest (90* knee and hip)
c. 12″ leg raises into abduction
d. Bicycling (knee up to chest, extend knee and sweep back to start with leg straight)
e. Clockwise circles
f. Counterclockwise circles
Good luck.
Trigger points in the piriformis muscle
The piriformis muscle is a small muscle deep to glute max and lies over top of the sciatic nerve. It originates on the anterior sacrum, and inserts on the greater trochanter of the femur. It’s main action is to laterally rotate the femur. When trigger points developed in this muscle they will refer pain into the sacro-iliac region, across the posterior hip and down the leg. This muscle can also be a cause of sciatic nerve irritation if it gets tight, causing “sciatica” symptoms. 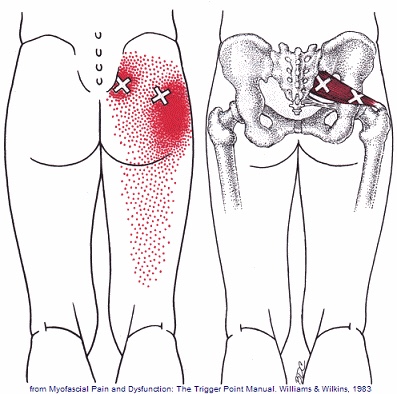
Trigger points in the gluteus medius muscle
The gluteus medius muscle plays an important role in hip and pelvic stability. It originates on the gluteal surface of the ilium, deep to the gluteus Maximus. It inserts on the greater trochanter of the femur. It’s main actions are to abduct the hip and to assist in internal rotation of the hip. It also maintains pelvic stability during walking and running. Trigger points in this muscle will refer pain into the sacrum, the iliac crest, and down the lateral hip and into the thigh. This muscle is often a cause of lower pack pain.
