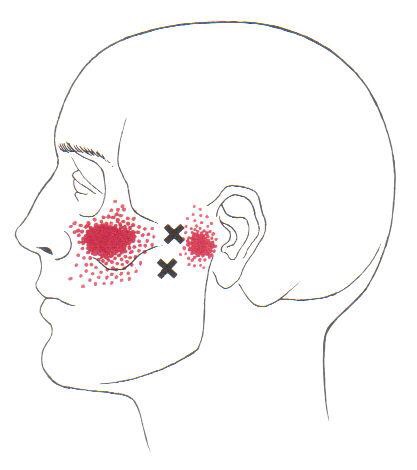
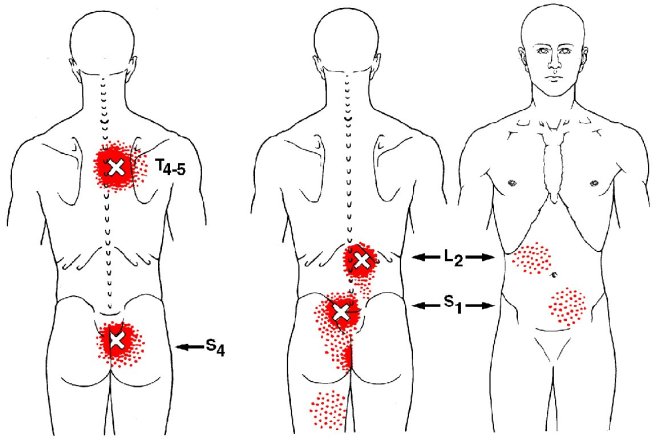
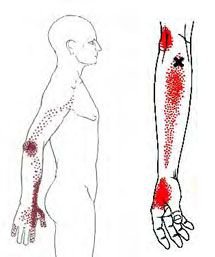
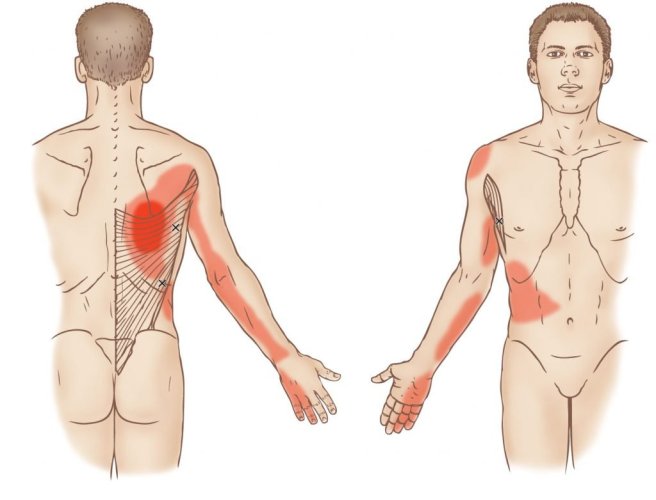
Trigger points form only in muscles. They form as a local contraction in a small number of muscle fibers in a larger muscle or muscle bundle. These in turn can pull on tendons and ligaments associated with the muscle and can cause pain deep within a joint where there are no muscles. The integrated hypothesis theory states that trigger points form from excessive release of acetylcholine which produces sustained depolarization of muscle fibers. Indeed, the trigger point has an abnormal biochemical composition with elevated concentrations of acetylcholine, noradrenaline and serotonin and a lower pH.[5] These sustained contractions of muscle sarcomeres compresses local blood supply restricting the energy needs of the local region. This crisis of energy produces sensitizing substances that interact with some nociceptive (pain) nerves traversing in the local region which in turn can produce localized pain within the muscle at the neuromuscular junction (Travell and Simons 1999). When trigger points are present in muscles there is often pain and weakness in the associated structures. These pain patterns in muscles follow specific nerve pathways and have been readily mapped to allow for identification of the causative pain factor. Many trigger points have pain patterns that overlap, and some create reciprocal cyclic relationships that need to be treated extensively to remove them.