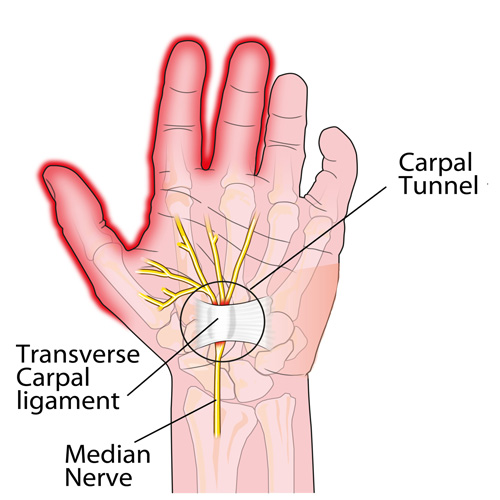
Carpal Tunnel
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome #3

This week, we will conclude our three-part series on important facts regarding carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS).
CTS TREATMENT OPTIONS (continued): Aside from the carpal tunnel, there are several places where the median nerve can become compressed as it travels from the neck, down through the shoulder, through tight muscular areas of the upper arm and forearm, and finally through the carpal tunnel at the wrist. In order to achieve good, long-lasting results, treatment must focus on relieving compression at any point along the course of the nerve. This is why chiropractic works SO WELL as it addresses ALL of these areas using manual adjustments, muscle release techniques, and even physical therapy modalities.
CTS PREVENTION: Because there are multiple causes of CTS, prevention must be tailored to each person. For example, if the patient has diabetes mellitus, maintaining a proper blood sugar level is very important because the blood becomes thicker as the sugar levels increase and it simply cannot pass through our small blood vessels (capillaries), especially those located in the feet and hands. This can eventually lead to the need for amputation due to poor circulation and contribute to the numbness associated with diabetic neuropathy.
Similarly, low thyroid function results in a type of swelling called myxedema that can cause or worsen CTS, and keeping the thyroid hormone balanced in the bloodstream is very important. Managing other conditions that create inflammation or swelling, such as rheumatoid and other types of arthritis, will also help prevent CTS from developing or worsening.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can also occur during pregnancy due to the hormonal shifts similar for those taking birth control pills. The PRICE treatment options presented last month can be very helpful for the pregnant mother and represent important non-medication self-care approaches.
Certain occupations that require fast, repetitive work and/or firm gripping can result in carpal tunnel syndrome because of the friction that results in swelling that occurs when the muscle tendons inside the carpal tunnel rub excessively fast together (kind of like starting a fire with two sticks). Modifying the work task until the swelling is controlled is VERY important, as discussed last month.
Other preventative measures include exercises that keep the muscles and tendons in the forearm and inside the carpal tunnel stretched so that the tendons easily slide inside their respective muscle tendon sheaths. This is accomplished by placing the palm side of the hand (elbow straight) on a wall with the fingers pointing downwards while reaching across with the opposite hand and pulling the thumb back until you feel a good firm stretch. Hold this position for 5-10 seconds or until the forearm muscles feel like they are relaxing. Repeat this multiple times a day.
We realize you have a choice in whom you consider for your health care provision and we sincerely appreciate your trust in choosing our service for those needs. If you, a friend, or family member requires care for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, we would be honored to render our services.
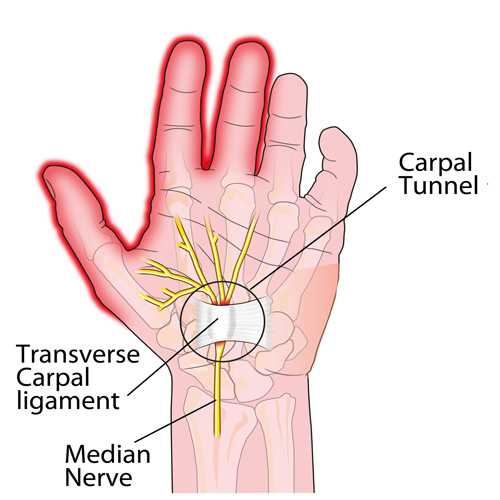
Carpel Tunnel in a nutshell
Here it is: carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) in a nutshell!

Do you have CTS?
Trigger points in the scalenes muscles
The scalenes muscles are located in the neck and help with neck movements and inspiration. The anterior scalene runs directly over the brachial plexus that gives nerve and blood supply to the arm. Poor neck and head posture as well as poor breathing mechanics can cause this muscle to become overloaded and develope trigger points. These points will refer pain into the shoulder, arm, and hand. As well as the shoulder blade. When tight, the anterior scalene muscle can put pressure on the brachial plexus causing numbness and tingling felt in the fingers and hand.

Brachioradialis trigger points and forearm and hand pain.
The Brachioradialis muscle is located in the forearm. It is responsible for flexing the elbow in semipronation such as when lifting a coffee mug up to your mouth. Trigger points in this muscle are an often overlooked source of elbow pain. These points will also refer pain down the forearm and into the web of the thumb.

Why trigger point therapy?
People often think of a massage as a relaxing experience, something they might do occasionally, or give as a gift along with a trip to the spa. Trigger point massage therapy is another kind of massage used to treat pain and physical dysfunction. Trigger points can develop in people from all walks of life. They can affect people of all ages, office workers and labourers, elite and weekend athletes, post surgical patients, people with acute pain from injury and people with chronic pain. Trigger point massage therapy can treat a wide variety of physical conditions such as:
– Migraines
– back pain.
– sciatica
– Carple tunnel syndrome
– achy persistent pain
– pain from Fibromyalgia
– post surgical pain and scarring
– soft tissue injuries related to sports
– TMJ dysfunction

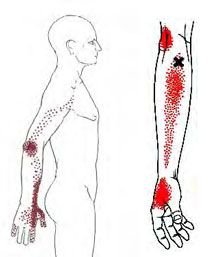
The brachioradialis muscle is located in your forearm, this muscle is responsible for helping to flex the elbow during semi pronation. Because of this it is sometimes called your drinking muscle. trigger points in this muscle will cause pain to refer into the elbow, down the forearm and into the hand. When severe enough trigger point pain can event travel up the arm.
Trigger point massage therapy.
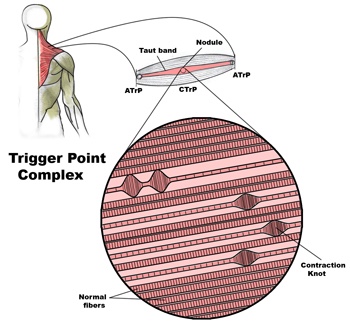
Trigger points are hyper irritable knots found in muscle tissue. These points form in a muscle due to overload stress. Trigger points can form anywhere, in any muscle. Once formed they irritate sensory nerves and produce pain, refered pain, weakness, and stiffness. Trigger points will also mimic symptoms of other conditions such as “sciatica” or Carple tunnel syndrome. Trigger points will not go away on there own, they must be manually released with hands on techniques like trigger point massage.

Trigger points.
Trigger points are knots of contracted muscle or connective tissue that form as a result of overload stress. Once formed these points will produce pain, refered pain, weakness, and stiffness. Trigger points can also mimic other conditions such as Carple tunnel syndrome and sciatica. Trigger points will on go away on their own, they must be manually released.