Myofascial pain syndrome (trigger points) and fibromyalgia are often confused to be the same condition and while there is a lot of interrelatedness between the two they are not quite identical. The clinical definition of a trigger point is “a hyper irritable spot associated within a taut band of skeletal muscle that is painful on compression or muscle contraction, and usually responds with a referred pain pattern distant from the spot”. Trigger points form from an overload trauma to the muscle tissue. This is contrasted with fibromyalgia which is defined as “a medical condition characterized by chronic widespread pain and a heightened pain response to pressure. Other symptoms include tiredness to a degree that normal activities are affected, sleep problems and troubles with memory. Some people also report restless leg syndrome, bowel and bladder problems, numbness and tingling and sensitivity to noise, lights and temperature. It is also associated with depression, anxiety, and post traumatic stress disorder”. Fibromyalgia will also present with localized tender points which are often mistaken for trigger points. Where these two conditions become somewhat interrelated is via the nervous system. Fibromyalgia patients suffer from a super-sensitization of the nervous system causing hyperirritability and pain. Myofascial trigger points can be caused by,or be the cause of, super sensitization. An active trigger point will irritate the sensory nerves around it eventually leading to super-sensitization. Trigger points have also been showed to form of become active due to super-sensitization. Both of these conditions can perpetuate the other, leading to layers of pain and symptoms. This being the case, trigger point therapy can have a very positive effect on decreasing the severity of pain and symptoms in patients suffering from fibromyalgia.

TMJ
Trigger points in the temporalis muscle
The temporalis muscle is located in the temple area of the skull. It originates on the temporal lines on the parietal bone of the skull, and inserts on the coronoid process of the mandible. It’s main action is to close the jaw. The posterior and middle fibres bilaterally retrude the mandible. Acting individually, this muscle will deviate the mandible to the same side. Trigger points in this muscle refer into the teeth causing hypersensitivity, and into and above the eye and temple, causing headaches.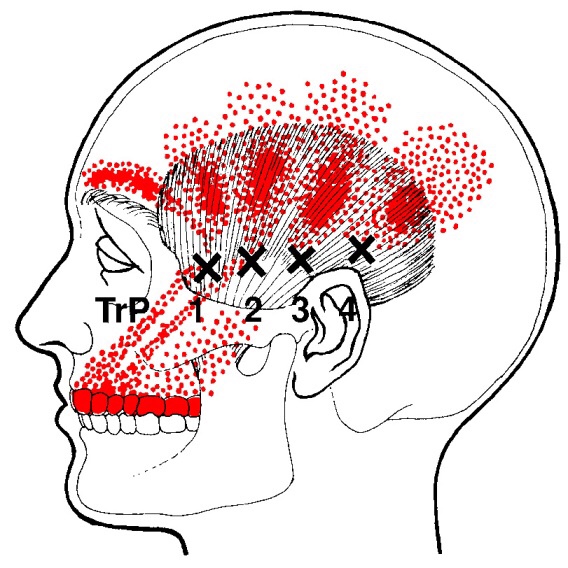
Trigger points in the lateral pterygoid
The lateral pterygoid muscle plays an important role in prober jaw function. It originates on the greater wing of the sphenoid bone and the lateral pterygoid plate, and inserts on the condyloid process of the mandible. It’s action is to pull the head of the mandibular condyle out of the mandibular fossa while opening the jaw. When trigger points develop they refer pain into the temporal mandibular joint and maxillary sinus. This referral is commonly mistaken for TM arthritis. In addition to the referral pain, trigger points in this muscle can also effect proper movement of the jaw.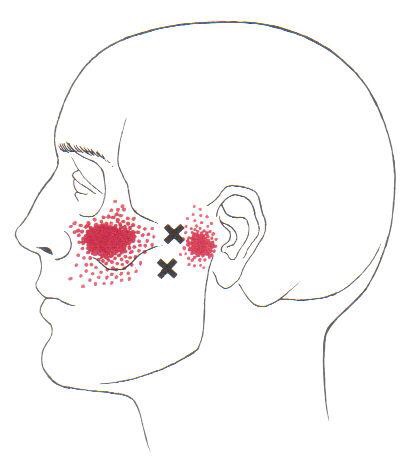

Pathophysiology of trigger points.
A large number of factors have been identified as causes of trigger point activation. These include acute or chronic overload of muscle tissue, disease, psychological distress, systemic inflammation, homeostatic imbalances, direct trauma, radiculopathy, infections, and lifestyle choices such as smoking. Trigger points form as a local contraction of muscle fibres in a muscle or bundle of muscle fibres. These can pull on ligaments and tendons associated with the muscle which can cause pain to be felt deep inside a joint. It is theorized that trigger points form from excessive release of acetylcholine causing sustained depolarization of muscle fibres. Trigger points present an abnormal biochemical composition with elevated levels of acetylcholine, noradrenaline and serotonin and a lower ph. The contracted fibres in a trigger point constricts blood supply to the area creating an energy crisis in the tissue that results in the production of sensitizing substances that interact with pain receptors producing pain. When trigger points are present in a muscle there is often pain and weakness in the associated structures. These pain patterns follow specific nerve pathways that have been well mapped to allow for accurate diagnosis or the causative pain factor.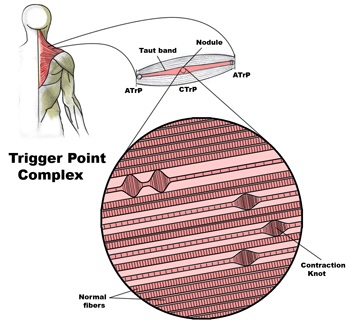
Diagnosis of trigger points.
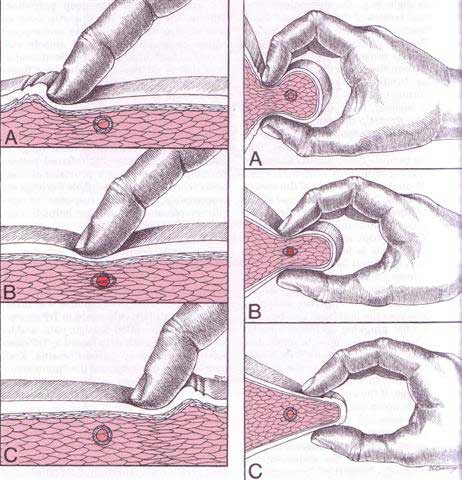
Diagnosis of trigger points typically takes into account symptoms, pain patterns, and manual palpation. When palpating the therapist will feel for a taut band of muscle with a hard nodule within it. Often a local twitch response will be elicited by running a finger perpendicular to the muscle fibres direction. Pressure applied to the trigger point will often reproduce the pain complaint of the patient and the referral pattern of the trigger point. Often there is a heat differential in the local area of the trigger point. 
What is a trigger point
Dr Janet travel coined the term trigger point in 1942 to describe clinical findings with characteristics of pain related a discrete irritable point in muscle or fascia that was not caused by acute trauma, inflammation, degeneration, neoplasm or infection. The painful point can be palpated as a nodule or tight band in the muscle that can produce a local twitch response when stimulated. Palpation of the trigger point reproduces the pain and symptoms of the patient and the pain radiates in a predictable referral pattern specific to the muscle harbouring the trigger point.
What to expect with a trigger point massage.
A treatment with Bryan is very user friendly. And, no, you don’t have to remove any clothing. However, bringing a t-shirt and a pair of shorts or sweats is recommended.
The first time you come for a treatment you will be asked to fill out a Client History form. Bryan will go over the information you provide, asking for more detail and discussing the type of pain you are having and its location.
The treatment itself involves locating the Trigger Points in the muscle or soft tissue and applying a deep focused pressure to the Point. This will reproduce the pain and the referral pattern that is characteristic of that pain.
The treatment will be uncomfortable at first, but as the Trigger Points release, the pain will decrease. The pressure will always be adjusted to your tolerance level. If, at any time, you feel too uncomfortable you can ask Bryan to ease off a bit.
Depending on your specific problem, Bryan may also use some stretching and / or range-of-motion techniques, as needed.
After treatment, it is usually recommended that the client apply moist heat to the area treated.
Have you Been Told You Have TMJ Disorder?
Temporomandibular Disorder (TMD) is a term used to describe a group problems that cause pain in the temporomandibular joint, also called the TMJ. These problems can arise from the muscles around the joint, the disc within the joint or the bony portion of the joint itself. Imbalances between the muscles that open and close your jaw are the most common culprit.

Up to 25% of the population will suffer with TMD symptoms. Most patients are 20-50 years old and the condition is 2-3 times more common in females. Typical symptoms include: jaw clicking, limited mouth opening, possible jaw locking and pain. Chewing and eating usually make your symptoms more noticeable. TMD pain is generally described as an “ache” located in front of your ear canal but may also refer to other areas of your face, head, neck and shoulders. TMD patients often suffer from headaches.
TMD is more common in people who clench their jaw or grind their teeth, especially at night. Bad posture and emotional stress are contributors to this problem. You are three times more likely to suffer with TMD if you have been involved in a “whiplash” accident.
Conservative treatments, like those provided by our office, have been shown to be as effective as any surgery for most patients with TMD. Treatment is simple, focusing on “massaging” tightness out of the jaw muscles, restoring movement to any restricted joints (including your neck and upper back), and prescribing exercises to improve flexibility.
You should avoid aggravating activities like chewing gum or eating “rubbery” foods. Limit excessive talking. A custom fitted mouth guard may be prescribed to help minimize grinding & clenching and promote relaxation of your jaw muscles at night. Patients with night-time symptoms should avoid stressful activity before bedtime and try to sleep in a “neutral” position. In some cases, stress management techniques, like biofeedback, can assist you in learning how to relax your jaw muscles.
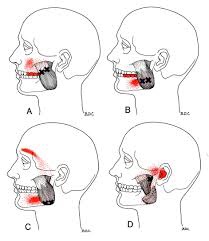
Trigger points in the masseter muscle

The masseter is the main muscle that moves your jaw. It originates on the zygomatic arch and maxilla, and inserts on the coronoid process and Ramus of the mandible. It’s actions are to elevate the mandible and close the jaw. The deep fibres of this muscle also retrude the mandible. This muscle commonly harbours trigger points as a result of teeth grinding. Trigger points in this muscle are often also associated with tmj dysfunction. Trigger points in the upper part of this muscle will refer pain to the upper molars and maxilla often felt as sinusitis. Trigger points in the lower portion of this muscle refer to the lower molars and temple. All trigger points can cause tooth sensitivity