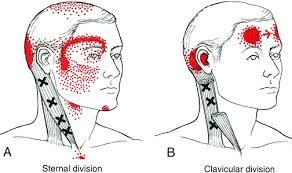
the sternocleidomastoid muscles are located in the front of the neck. these muscles are often overworked from prolonged sitting posture. Trigger points in these muscles are a common cause of headache pain.

the sternocleidomastoid muscles are located in the front of the neck. these muscles are often overworked from prolonged sitting posture. Trigger points in these muscles are a common cause of headache pain.

trigger points are one of the most common sources of pain in the body. Once a trigger point has formed it won’t release on its own. Trigger point massage is one of the most effective way to release a point. It involves using a deep focused pressure applied directly to the knot. This frees the contracted tissue and stimulates healing.
Myofascial trigger points form in a muscle due to overload stress. A portion of muscle fibers lock up into a knot. Once formed these points will irritate sensory nerves that are in proximity to the knot. When this happens,

trigger points have the capacity to refer pain along specific distributions or patterns that are well mapped out. sometimes pain may be felt at a great distance away from the actual point itself.
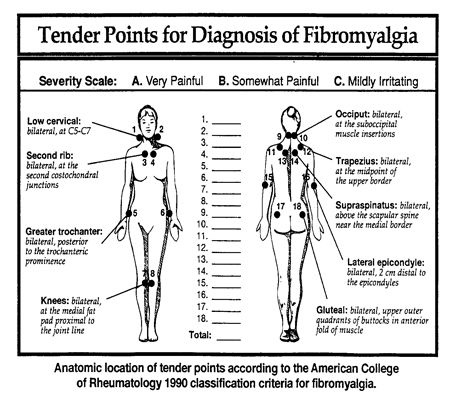
Trigger points are knots of contracted muscle or connective tissue that form as a result of overload stress. Once formed these points will produce pain, refered pain, weakness, and stiffness. Trigger points can also mimic other conditions such as Carple tunnel syndrome and sciatica. Trigger points will on go away on their own, they must be manually released.

The sternocleidomastoid muscles are two strap like muscles located in the front of you neck. They often become overworked from poor sitting posture. Trigger points in these muscles will cause referral pain into the head and around the eye, causing migraine type pain.

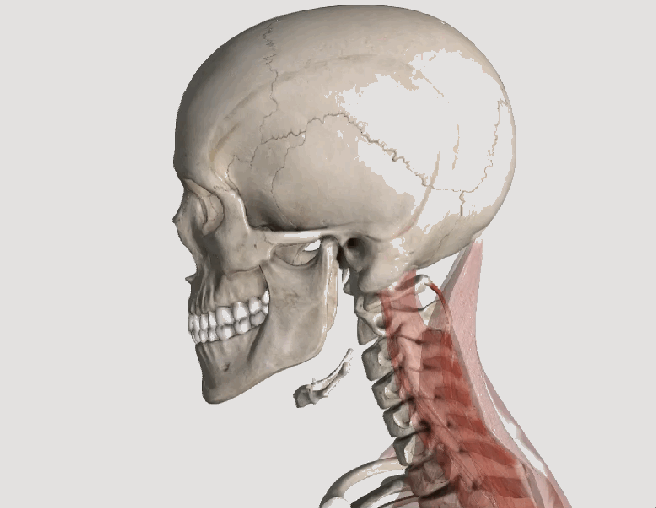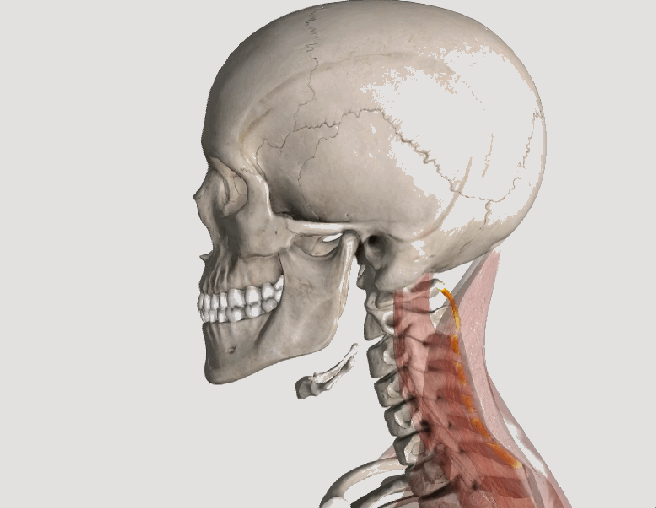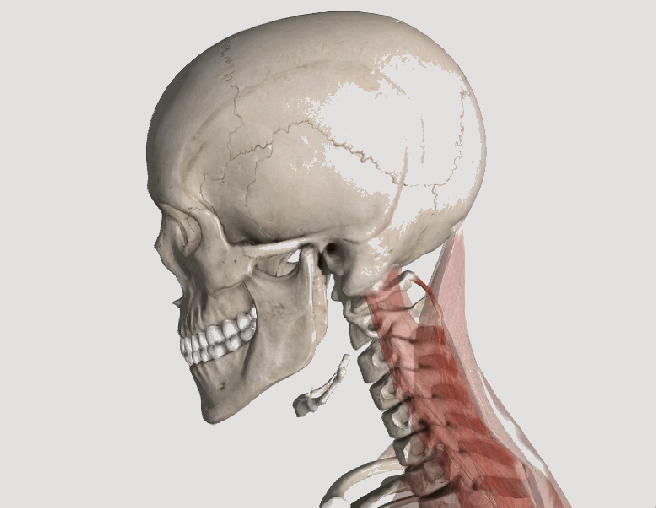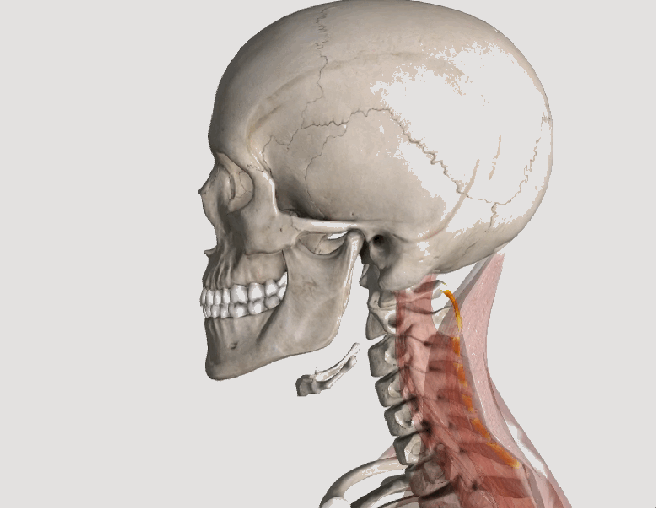
The trapezius muscle is a large diamond shaped muscle located in your back. This muscle is often overloaded due to poor sitting posture or excessive exercise. When this occurs trigger points will form. These points can cause back, neck, and shoulder pain. Trigger points in the upper traps are a leading cause of headache.

Whiplash is really a slang term for the rapid back and forth whipping of the head on the neck, usually associated with motor vehicle accidents. The title “Whiplash Associated Disorders”, or WAD, describes it best because it includes ALL of the MANY signs and symptoms of the disorder.
WAD basically comes in three sizes based on the degree of injury. A WAD I is present when there is pain but no physical examination findings; WAD II occurs when there are exam findings but no neurological loss (numbness or weakness); and WAD III includes loss of neurological function. There is also a separate WAD level that includes fractures and dislocations (WAD IV).
There are many things that can be done by the patient to assist in the healing process for WAD. The first well-studied recommendation is to “continue with your usual activities.” Try to keep active and not change your routine. The good news is that WAD (especially types I and II) usually resolves without complication, and recovery is even more likely to occur if you don’t deviate much from your routine.
For those whose symptoms are more severe and/or not resolving, mobilization and manipulation of the neck and back are very effective treatment options. In addition to treatments you’d receive in a chiropractic office, there are MANY things you can do at home as “self-help strategies.” Some of these include (“PRICE”):
1) PROTECT: Though it’s important to continue with your usual daily activities, this is dependent on both the degree of tissue injury and your pain tolerance. So do as many of your usual daily activities as possible, but AVOID those that result in a sharp, lancinating type of pain or those where recovery from the pain is delayed. Therefore, this category may require modifying your ADLs (activities of daily living). A cervical collar (hard or
soft) should NOT to be used UNLESS you have an unstable injury (fracture or a grade III sprain).
2) REST: Doing too much is like picking at a cut (which can delay healing) and doing too little can lead to a delayed healing response as well. Staying within reasonable pain boundaries is a good guide.
3) ICE > HEAT: Ice reduces swelling, and your doctor will typically recommend it over applying heat, especially on a recent injury. Heat draws fluids in, and while it may feel good, it can make your symptoms worse.
4) COMPRESS: We can basically ignore this when referencing neck pain. This pertains better to wrapping an ankle, knee, wrist, or elbow with an elastic compression orthotic or brace.
5) ELEVATE: This too is meant for the acute stages of an extremity injury like a foot or ankle.
Exercises unique for neck pain in the acute, subacute, and chronic stages of healing are perhaps the most important of the self-help approaches. In the ACUTE phase, try these…
1) Range of Motion: Once again, stay within “reasonable pain boundaries” as you move your head forwards, backwards, side to side, and rotate left and right. These can be done either with or without LIGHT resistance applied using one or two fingers placed against your head. Limit the repetitions to three slow reps in each direction and emphasize the release of the movement.
2) Chin/head Glides: Tuck in the chin (think of creating a double or triple chin) followed by poking the chin/head out.
In the SUBACUTE and CHRONIC phases of healing, the importance of strengthening the deep neck flexors cannot be over emphasized. Please refer to last month’s article for a description of this (see #3 of the 6 recommendations listed).

Whiplash, or better termed “Whiplash Associated Disorders” (WAD), is a condition that carries multiple signs and symptoms ranging from neck pain and stiffness to headache, confusion, ringing in the ears, and more. But can WAD cause dizziness? Let’s take a look!
Dizziness is a general term that is used rather loosely by the general population. We’ve all experienced dizziness from time-to-time that is considered “normal,” such as standing up too quickly or while experiencing a rough flight.
Often, dizziness and problems with balance go hand in hand. There are three main organs that control our balance: 1) the vestibular system (the inner ear); 2) the cerebellum (lies in the back of the head); and, 3) the dorsal columns (located in the back part of the spinal cord). In this article, we will primarily focus on the inner ear because, of the three, it’s unique for causing dizziness. Our vision also plays an important role in maintaining balance, as we tend to lose our balance much faster when we close our eyes.
It’s appropriate to first discuss the transient, usually short episode of “normal” lightheadedness associated with rising quickly. This is typically caused by a momentary drop in blood pressure, and hence, oxygen simply doesn’t reach the brain quick enough when moving from sitting to standing. Again, this is normal and termed “orthostatic hypotension” (OH).
However, OH can be exaggerated by colds, the flu, allergy flair-ups, when hyperventilating, or at times of increased stress or anxiety. OH is also associated with the use of tobacco, alcohol, and/or some medications. Bleeding can represent a more serious cause of OH such as with bleeding ulcers or some types of colitis, and less seriously, with menstruation.
The term BPPV or benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, has to do with the inner ear where our semicircular canals are located. The canals lie in three planes and give us a 3D, 360º perspective about where we are in space. The fluid flowing through these canals bends little hair-like projections, which are connected to sensory nerves that tell the brain about our spatial position. If the function of these canals is disturbed, it can mix-up the messages the brain receives, thus resulting in dizziness. Exercises are available on the Internet that can help with BPPV (look for Epley’s and Brandt-Daroff exercises).
DANGEROUS causes of dizziness include: HEART – fainting (passing out) accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, pain or pressure in the back, neck, jaw, upper belly, or in one or both arms, sudden weakness, and/or a fast or irregular heartbeat. STROKE – sudden numbness, paralysis, or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially if only on one side of the body; drooling, slurred speech, short “black outs,” sudden visual changes, confusion/difficulty speaking, and/or a sudden and severe, “out of the ordinary” headache. CALL 911 (or the number for emergency services if you’re outside the United States) if you suspect you may be having a heart attack or stroke!
Session Description
A treatment with Bryan is very user friendly. And, no, you don’t have to remove any clothing. However, bringing a t-shirt and a pair of shorts or sweats is recommended.
The first time you come for a treatment you will be asked to fill out a Client History form. Bryan will go over the information you provide, asking for more detail and discussing the type of pain you are having and its location.
The treatment itself involves locating the Trigger Points in the muscle or soft tissue and applying a deep focused pressure to the Point. This will reproduce the pain and the referral pattern that is characteristic of that pain.
The treatment will be uncomfortable at first, but as the Trigger Points release, the pain will decrease. The pressure will always be adjusted to your tolerance level. If, at any time, you feel too uncomfortable you can ask Bryan to ease off a bit.
Depending on your specific problem, Bryan may also use some stretching and / or range-of-motion techniques, as needed.
After treatment, it is usually recommended that the client apply moist heat to the area treated.



Neck pain is very common! According to one study, between 10-21% of the population will experience an episode of neck pain each year with a higher incidence rate among office workers. Between 33-65% will recover within one year, but most cases become “chronic, recurrent” meaning neck pain will come and go indefinitely. The more we can learn WHAT to do to prevent these episodes, the better.
1. SLEEP: Use a cervical pillow so the NECK is fully supported during sleep. This keeps your head in alignment with your spine. Also, if possible, sleep on your back!
2. OFFICE: Position the computer screen so that it’s at or slightly below eye level and straight in front of you. The “KEY” point is that you feel comfortable with the height of the monitor. Keep your chin “tucked in” so the 10-11 pound (4.5-5 kg) weight of your head stays back over your shoulders—this will place less of a load on your upper back and neck muscles to hold your head upright! Set a timer on your cell phone to remind you to get up and move around every 30-60 minutes.
3. TELEPHONE: If you are using the phone a lot during the day, GET A HEADSET! If you are pinching the phone between your shoulder and ear, you WILL have neck problems!
4. EXERCISE: Studies show people who are more physically active are less likely to report neck pain.
5. NUTRITION: Search for information on the “anti-inflammatory diet.” It’s basically fruits, veggies, and lean meat, with a few other twists. Also, stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water each day.
6. LIFT/CARRY: A heavy purse, brief case, or roller bag can really hurt your neck. Take ONLY what you need and put the rest in a secondary bag that stays in your car or where you can access it when needed. Switch to a backpack if possible vs. a heavy brief case.
7. SELF-MASSAGE: Reach back and dig your fingers into your neck muscles and “work” the tight fibers back and forth until they loosen up. Roll your head over the top edge of a chair by sliding down until the top of the chair back rests in your neck. Search for the tight fibers and work them loose!
8. WHIPLASH: If you are injured, DO NOT WAIT! Those who seek chiropractic care shortly after an accident have less long-term trouble!