Your spine consists of 24 individual vertebrae stacked on top of each other. Flexible cushions called “discs” live between each set of vertebrae. A disc is made up of two basic components. The inner disc, called the “nucleus”, is like a ball of jelly about the size of a marble. This jelly is held in place by the outer part of the disc called the “annulus”, which is wrapped around the inner nucleus much like a ribbon wrapping around your finger. The term lumbar disc lesion means that your disc has been damaged.


Disc lesions start when the outer fibers of the disc become strained or frayed. If enough fibers become frayed, this can create a weakness and when the disc is compressed, the outer fibers may “bulge” or “protrude” like a weak spot on an inner tube. If more fibers are damaged, the nucleus of the disc may “herniate” outward. Since the spinal cord and nerve roots live directly behind the disc, bulges that are accompanied by inflammation will likely create lower back pain that radiates into the buttock or the entire lower extremity. This condition is called sciatica. If the disc bulge is significant enough to create a mechanical compression of your nerve, you may also experience loss of your reflexes and weakness. Be sure to let our office know if you notice progressive weakness or numbness, any numbness around your groin, any loss of bowel or bladder control or fever.
Surprisingly, disc bulges are present without any symptoms in about 1/3 of the adult population. Another one third of adults will experience pain from a lumbar disc at some point in their lifetime. The condition is more common in men. Most lumbar disc problems occur at one of the two lowest discs- L5 or L4. Smokers and people who are generally inactive have a higher risk of lumbar disc problems. Certain occupations may place you at a greater risk, especially if you spend extended periods of time sitting or driving. People who are tall or overweight have increased risk of disc problems. The condition is uncommon in children and is most common between the ages of 40 and 60.
Researches have shown that disc bulges and sciatica may be successfully managed with conservative care like the type we will provide.

 Your low back relies on discs and other ligaments for support. “Discogenic Low Back Pain” develops when these tissues are placed under excessive stress, much like a rope that frays when it is stretched beyond its normal capacity. Most commonly, disc pain is not the result of any single event, but rather from repeated overloading. Your lumbar discs generally manage small isolated stressors quite well, but repetitive challenges lead to injury in much the same way that constantly bending a piece of copper wire will cause it to break. Examples of these stressors include: bad postures, sedentary lifestyles, poor fitting workstations, repetitive movements, improper lifting, or being overweight.
Your low back relies on discs and other ligaments for support. “Discogenic Low Back Pain” develops when these tissues are placed under excessive stress, much like a rope that frays when it is stretched beyond its normal capacity. Most commonly, disc pain is not the result of any single event, but rather from repeated overloading. Your lumbar discs generally manage small isolated stressors quite well, but repetitive challenges lead to injury in much the same way that constantly bending a piece of copper wire will cause it to break. Examples of these stressors include: bad postures, sedentary lifestyles, poor fitting workstations, repetitive movements, improper lifting, or being overweight.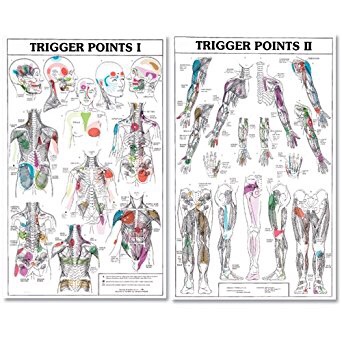


 tough, durable ligaments that hold your bones together have been damaged, while “strain” means that your muscles or tendons that move your trunk have been partially torn.
tough, durable ligaments that hold your bones together have been damaged, while “strain” means that your muscles or tendons that move your trunk have been partially torn.
 Weakness of the gluteus medius allows your pelvis to drop and your knee to dive inward when you walk or run. This places tremendous strain on your hip and knee and may cause other problems too. When your knee dives inward, your kneecap is forced outward, causing it to rub harder against your thigh bone- creating a painful irritation and eventually arthritis. Walking and running with a relative “knock knee” position places tremendous stress on the ligaments around your knee and is a known cause of “sprains”. Downstream, a “knock knee” position puts additional stress on the arch of your foot, leading to other painful problems, like plantar fasciitis. Upstream, weak hips allow your pelvis to roll forward which forces your spine into a “sway back” posture. This is a known cause of lower back pain. Hip muscle weakness seems to be more common in females, especially athletes.
Weakness of the gluteus medius allows your pelvis to drop and your knee to dive inward when you walk or run. This places tremendous strain on your hip and knee and may cause other problems too. When your knee dives inward, your kneecap is forced outward, causing it to rub harder against your thigh bone- creating a painful irritation and eventually arthritis. Walking and running with a relative “knock knee” position places tremendous stress on the ligaments around your knee and is a known cause of “sprains”. Downstream, a “knock knee” position puts additional stress on the arch of your foot, leading to other painful problems, like plantar fasciitis. Upstream, weak hips allow your pelvis to roll forward which forces your spine into a “sway back” posture. This is a known cause of lower back pain. Hip muscle weakness seems to be more common in females, especially athletes. When a facet is irritated, you will likely notice pain on one side of your back that may radiate into your flank, hip, and thigh. The pain may come and go. Your pain may increase when you arch backwards or return to an upright position after bending forward. Many patients report relief when they lie down. Symptoms of facet syndrome do not usually radiate past your knee. Be sure to tell your chiropractor if your symptoms include any radiation of pain below your knee, weakness, groin numbness, changes in bowel or bladder function, or if you have a fever.
When a facet is irritated, you will likely notice pain on one side of your back that may radiate into your flank, hip, and thigh. The pain may come and go. Your pain may increase when you arch backwards or return to an upright position after bending forward. Many patients report relief when they lie down. Symptoms of facet syndrome do not usually radiate past your knee. Be sure to tell your chiropractor if your symptoms include any radiation of pain below your knee, weakness, groin numbness, changes in bowel or bladder function, or if you have a fever. This nerve can be compressed beneath a ligament, tendon or tight muscle in your hip and pelvis. Pregnancy or being even slightly overweight makes this condition more likely. Tight clothing including girdles, compressive shorts, or tight belts may aggravate or cause this condition. Carpenters’ tool belts or police duty belts may compress this nerve. Prolonged sitting or lying in a fetal position may aggravate this problem. Diabetics are at greater risk.
This nerve can be compressed beneath a ligament, tendon or tight muscle in your hip and pelvis. Pregnancy or being even slightly overweight makes this condition more likely. Tight clothing including girdles, compressive shorts, or tight belts may aggravate or cause this condition. Carpenters’ tool belts or police duty belts may compress this nerve. Prolonged sitting or lying in a fetal position may aggravate this problem. Diabetics are at greater risk. Your lower back is made up of 5 bones stacked on top of each other with a soft “disc” between each segment to allow for flexibility. Normally, each joint in your spine should move freely and independently. Our examination of your spine has shown that one or more of the joints in your low back is slightly misaligned and restricted. We call this condition “lumbar segmental joint restriction”.
Your lower back is made up of 5 bones stacked on top of each other with a soft “disc” between each segment to allow for flexibility. Normally, each joint in your spine should move freely and independently. Our examination of your spine has shown that one or more of the joints in your low back is slightly misaligned and restricted. We call this condition “lumbar segmental joint restriction”.