Due to bipedal locomotion (walking around on two legs), foot and ankle problems have the potential to affect EVERYTHING above the feet—even the knees!
When analyzing the way we walk (also known as our gait), we find when the heel strike takes place, the heel and foot motion causes “supination” or the rolling OUT of the ankle. As the unloaded leg begins to swing forwards, there is a quick transition to pronation where the heel and ankle roll inwards and the medial longitudinal arch (MLA) of the foot flattens and pronates NORMALLY!
During the transition from supination to pronation, the flattening of the MLA acts like a spring to propel us forwards followed by the “toe off”, the last phase, as we push off with our big toe and the cycle starts with the other leg. However, if you watch people walk from behind, you will see MANY ankles roll inwards too much. This is call “hyperpronation” and that is NOT NORMAL!
So at what point does this normal pronation become hyperpronation? The answer is NOT black and white, as there is no specific “cut-off” point but rather, a range of abnormal. Hence, we use the terms mild, moderate, and severe hyperpronation to describe the variance or the degrees of abnormality. Hyperpronation can lead to the development of bunions and foot/ankle instability that can cause and/or contribute to knee, hip, pelvis, and spinal problems—even neck and head complaints can result (the “domino effect”)!
One study looked at the incidence of hyperpronation in 50 subjects who had an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture vs. 50 without a history of knee / ACL injury. They found the ACL-injured subjects had greater pronation than the noninjured subjects suggesting that the presence of hyperpronation increases the risk of ACL injury.
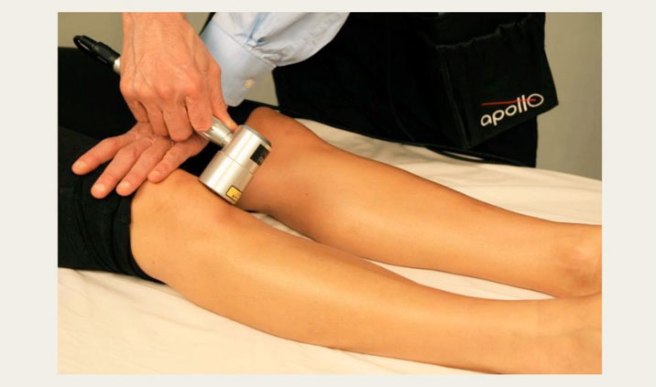
Doctors of chiropractic are trained to evaluate and treat knee conditions of all kinds. Often this may include prescribing exercises or utilizing foot orthotics in an effort to restore the biomechanics of the foot, which can have positive effects not only on the knees but also further up the body.