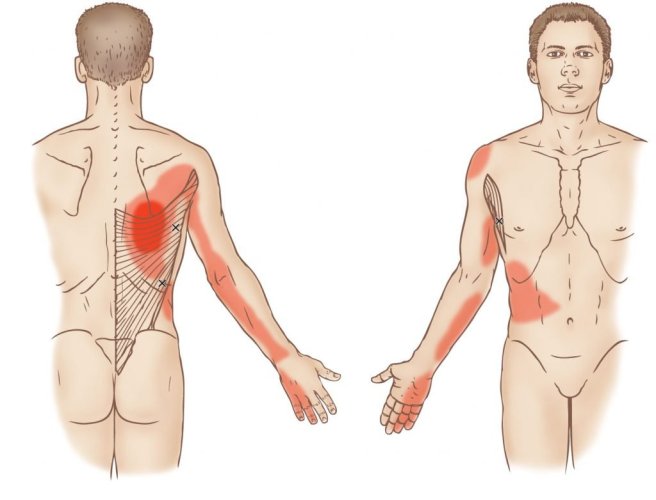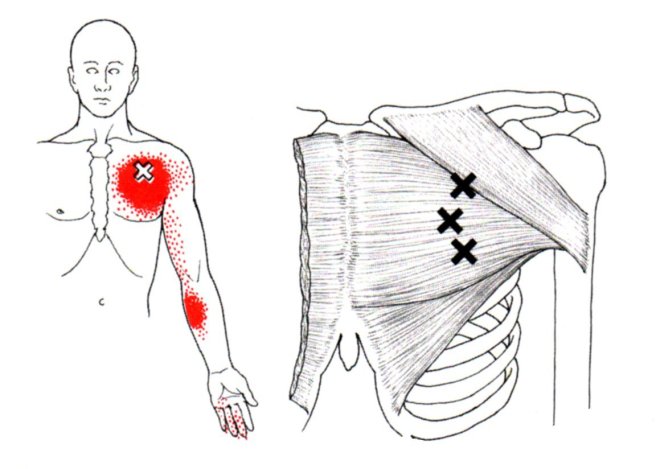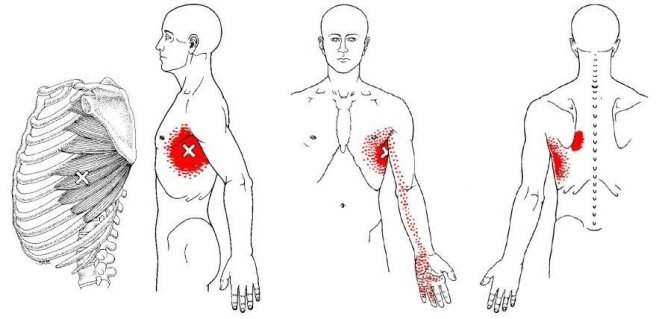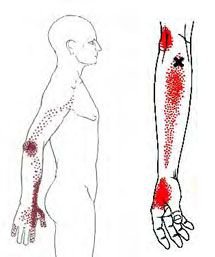
The brachioradialis muscle is located in your forearm, this muscle is responsible for helping to flex the elbow during semi pronation. Because of this it is sometimes called your drinking muscle. trigger points in this muscle will cause pain to refer into the elbow, down the forearm and into the hand. When severe enough trigger point pain can event travel up the arm.