Why Does My Back Hurt?



What is a Trigger Point?
Trigger Points (TP’s) are defined as a “hyper-irritable spot within a taut band of skeletal muscle. The spot is painful on compression and can evoke characteristic referred pain and autonomic phenomena.”1
Put into plain language, a TP is a painful knot in muscle tissue that can refer pain to other areas of the body. You have probably felt the characteristic achy pain and stiffness that TP’s produce, at some time in your life.
TP’s were first brought to the attention of the medical world by Dr. Janet G. Travell. Dr. Travell, physician to President John F. Kennedy, is the acknowledged Mother of Myofascial Trigger Points. In fact, “Trigger Point massage, the most effective modality used by massage therapists for the relief of pain, is based almost entirely on Dr. Travell’s insights.”2 Dr. Travell’s partner in her research was Dr. David G. Simons, a research scientist and aerospace physician.
Trigger Points are very common. In fact, Travell and Simons state that TP’s are responsible for, or associated with, 75% of pain complaints or conditions.1 With this kind of prevalence, it’s no wonder that TP’s are often referred to as the “scourge of mankind”.
Trigger Points can produce a wide variety of pain complaints. Some of the most common are migraine headaches, back pain, and pain and tingling into the extremities. They are usually responsible for most cases of achy deep pain that is hard to localize.
A TP will refer pain in a predictable pattern, based on its location in a given muscle. Also, since these spots are bundles of contracted muscle fibres, they can cause stiffness and a decreased range of motion. Chronic conditions with many TP’s can also cause general fatigue and malaise, as well as muscle weakness.
Trigger Points are remarkably easy to get, but the most common causes are
TP’s (black X) can refer pain to other areas (red)
Sudden overload of a muscle
Once in place, a TP can remain there for the remainder of your life unless an intervention takes place.
Trigger Points Not Well Known
With thousands of people dealing with chronic pain, and with TP’s being responsible for — or associated with — a high percentage of chronic pain, it is very disappointing to find that a large portion of doctors and other health care practitioners don’t know about TP’s and their symptoms.
Scientific research on TP’s dates back to the 1700’s. There are numerous medical texts and papers written on the subject.
But, it still has been largely overlooked by the health care field. This has led to needless frustration and suffering, as well as thousands of lost work hours and a poorer quality of life.
How Are Trigger Points Treated?
As nasty and troublesome as TP’s are, the treatment for them is surely straight-forward. A skilled practitioner will assess the individual’s pain complaint to determine the most likely location of the TP’s and then apply one of several therapeutic modalities, the most effective of which is a massage technique called “ischemic compression”.
Basically, the therapist will apply a firm, steady pressure to the TP, strong enough to reproduce the symptoms. The pressure will remain until the tissue softens and then the pressure will increase appropriately until the next barrier is felt. This pressure is continued until the referral pain has subsided and the TP is released. (Note: a full release of TP’s could take several sessions.)
Other effective modalities include dry needling (needle placed into the belly of the TP) or wet needling (injection into the TP). The use of moist heat and stretching prove effective, as well. The best practitioners for TP release are Massage Therapists, Physiotherapists, and Athletic Therapists. An educated individual can also apply ischemic compression to themselves, but should start out seeing one of the above therapists to become familiar with the modality and how to apply pressure safely.
1 Simons, D.G., Travell, D.G., & Simons, L.S. Travell and Simons’Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: the Trigger Point Manual.
Vol. 1. 2nd ed. Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins, 1999.
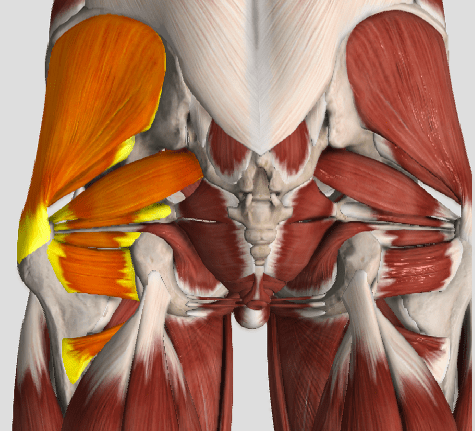
The muscles of the hip provide not only local stability, but also play an important role in spinal and lower extremity functional alignment. (1-4) While weakness in some hip muscles (hip extensors and knee extensors) is well tolerated, weakness or imbalance in others can have a profound effect on gait and biomechanical function throughout the lower half of the body. (5) Weakness of the hip abductors, particularly those that assist with external rotation, has the most significant impact on hip and lower extremity stability. (5,6)
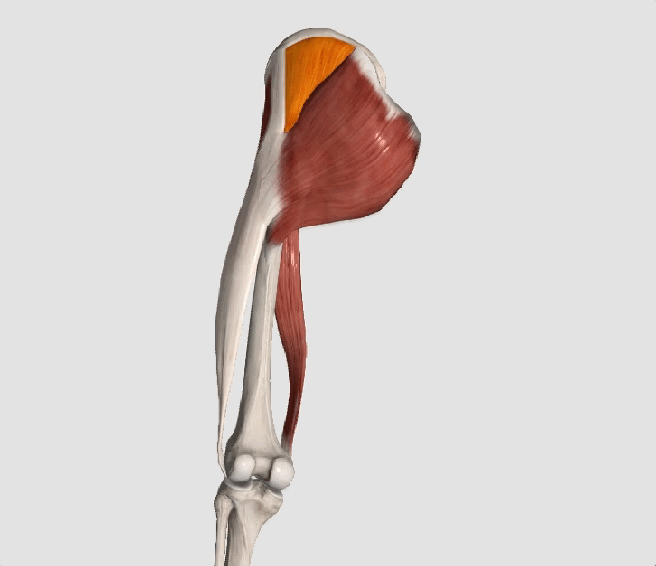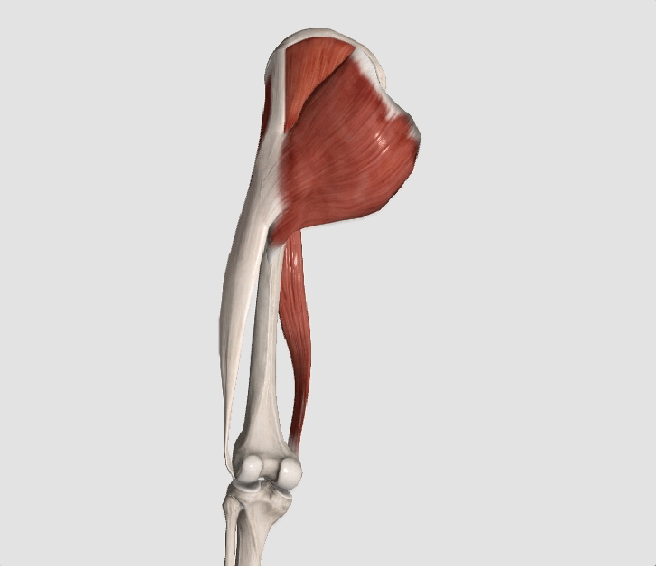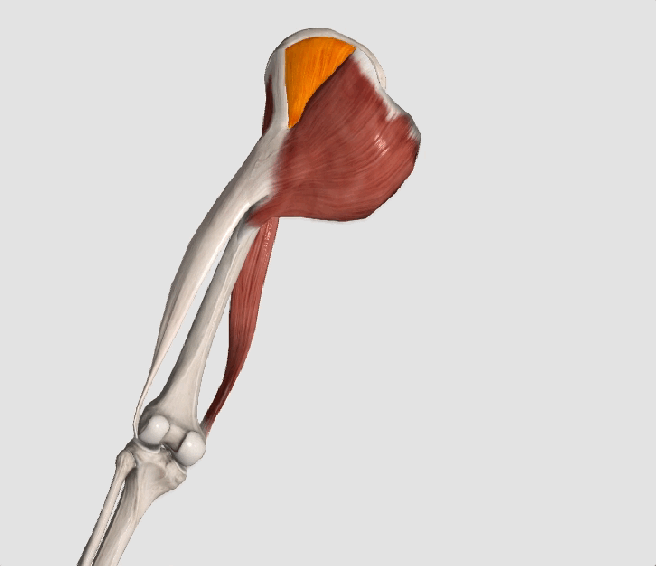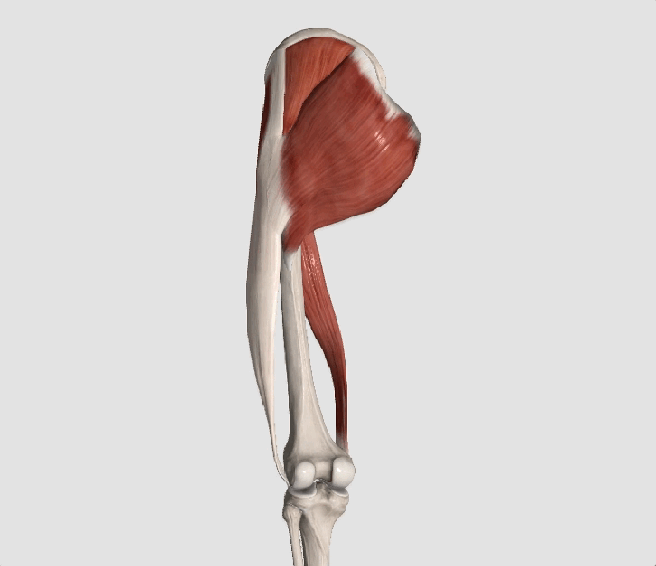
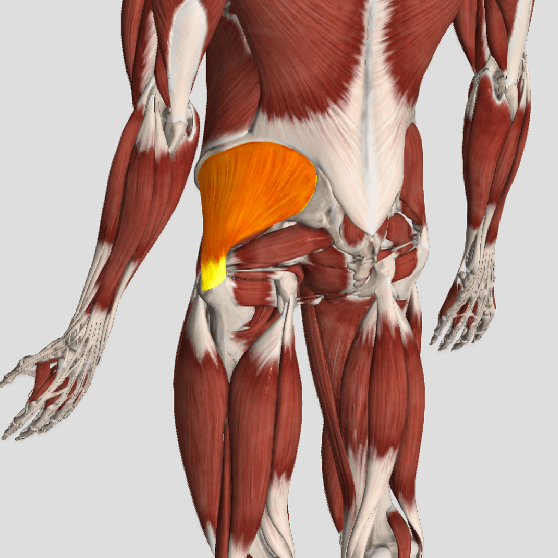
The gluteus medius is the principal hip abductor. When the hip is flexed, the muscle also assists the six deep hip external rotators (piriformis, gemelli, obturators, and quadratus femoris). The gluteus medius originates on the ilium just inferior to the iliac crest and inserts on the lateral and superior aspects of the greater trochanter. While the principal declared action of the gluteus medius is hip abduction, clinicians will appreciate its more valuable contribution as a dynamic stabilizer of the hip and pelvis- particularly during single leg stance activities like walking, running, and squatting. The gluteus medius contributes approximately 70% of the abduction force required to maintain pelvic leveling during single leg stance. The remainder comes predominantly from 2 muscles that insert onto the iliotibial band: the tensor fascia lata and upper gluteus maximus. Hip abductor strength is the single greatest contributor to lower extremity frontal plain alignment during activity. (6)
Incompetent hip abductors and/or external rotators allows for excessive adduction and internal rotation of the thigh during single leg stance activities. This leads to a cascade of biomechanical problems, including pelvic drop, excessive hip adduction, excessive femoral internal rotation, valgus knee stress, and internal tibial rotation. (1,7-12)

Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), also called “Runners Knee”, describes the symptom complex of knee discomfort, swelling, or crepitus that results from excessive or imbalanced forces acting on the joint. It is the most common cause of knee pain in the general population, affecting an estimated 25% of adults.
PFPS is most commonly related to lateral tracking of the patella. The patella has a natural tendency to migrate laterally due to the pull of the quadriceps and the slight natural valgus of the lower extremity. A new study in the Journal of Sports Medicine (1) provides additional confirmation that when managing patellofemoral pain syndrome, clinicians must address two critical yet often overlooked issues.
This study concludes that PFPS and dynamic knee valgus do not arise primarily from knee dysfunction, rather from hip abductor/ external rotator weakness and/or foot hyperpronation.
“The most effective intervention programs included exercises targeting the hip external rotator and abductor muscles and knee extensor muscles.” and “PFPS patients with foot abnormalities, such as those with increased rearfoot eversion or pes pronatus, may benefit the most from foot orthotics.”
Since gluteus medius and VMO weakness are key factors in the development of PFPS, strengthening exercises that target those muscles prove most effective. Stabilization exercises may include pillow push (push the back of your knee into a pillow for 5-6 seconds), supine heel slide, terminal knee (short-arc) extension, clam, glut bridge, semi-stiff deadlift, posterior lunge, and monster walk.
Myofascial release and stretching should be directed at hypertonic muscles, including the TFL, gastroc, soleus, hamstring, piriformis, hip rotators, and psoas. Myofascial release or IASTM may be appropriate for tightness in the iliotibial band, vastus lateralis, posterior hip capsule, and lateral knee retinaculum.
Manipulation may be necessary for restrictions in the lumbosacral and lower extremity joints. Hypermobility is common in the ipsilateral SI joint with restrictions present contralaterally. Evidence has shown that patellar tracking braces, i.e. BioSkin® or PatellaPro®, may lead to better outcomes.
Lifestyle modification may be necessary to reduce pain-provoking endeavors, especially running, jumping and other activities that induce a valgus stress. Athletes should avoid allowing their knee to cross in front of their toes while squatting. Arch supports or custom orthotics may be necessary to correct hyperpronation. Runners should avoid cross-over gaits and change shoes every 250 to 500 miles.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
#pain
#kneepain
#chiropractic
#fitness
#sports
#wellness
#fitness
#healthyliving
#healthychoices
#Winnipeg
References
1. Petersen W, Rembitzki I, Liebau C. Patellofemoral pain in athletes. Open Access Journal of Sports Medicine. 2017;8:143-15

Whiplash Associated Disorders (WAD) is the appropriate terminology to use when addressing the myriad of symptoms that can occur as a result of a motor vehicle collision (MVC). In a recent publication in The Physician and Sports Medicine (Volume 43, Issue 3, 2015; 7/3/15 online:1-11), the article “The role of the cervical spine in post-concussive syndrome” takes a look at the neck when it’s injured in a car accident and how this relates to concussion.
It’s estimated about 3.8 million concussion injuries, also referred to as “mild traumatic brain injury” (mTBI), occur each year in the United States. Ironically, it’s one of the least understood injuries in the sports medicine and neuroscience communities. The GOOD NEWS is that concussion symptoms resolve within 7-10 days in the majority of cases; unfortunately, this isn’t the case with 10-15% of patients. Symptoms can last weeks, months, or even years in this group for which the term “post-concussive syndrome” (PCS) is used (defined as three or more symptoms lasting for four weeks as defined by the ICD-10) or three months following a minor head injury (as defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders).
There have been significant advances in understanding what takes place in the acute phase of mTBI, but unfortunately, there is no clear physiological explanation for the chronic phase. Studies show the range of force to the head needed to cause concussion is between 60-160g (“g” = gravity) with 96.1g representing the highest predictive value in a football injury, whereas as little as 4.5g of neck acceleration can cause mild strain injury to the neck. In spite of this difference, the signs and symptoms reported by those injured in low-speed MVCs vs. football collisions are strikingly similar!
Research shows if an individual sustains an injury where the head is accelerated between 60-160g, it is HIGHLY likely that the tissues of the cervical spine (neck) have also reached their injury threshold of 4.5g. In a study that looked at hockey players, those who sustained a concussion also had WAD / neck injuries indicating that these injuries occur concurrently. Injuries to the neck in WAD include the same symptoms that occur in concussion including headache, dizziness/balance loss, nausea, visual and auditory problems, and cognitive dysfunction, just to name a few.
The paper concludes with five cases of PCS that responded well to a combination of active exercise/rehabilitation AND passive manual therapy (cervical spine manipulation). The favourable outcome supports the concept that the neck injury portion of WAD is a very important aspect to consider when treating patients with PCS!
This “link” between neck injury and concussion explains why chiropractic care is essential in the treatment of the concussion patient! This is especially true when the symptoms of concussion persist longer than one month!
We realize you have a choice in whom you consider for your health care provision and we sincerely appreciate your trust in choosing our service for those needs. If you, a friend, or family member requires care for Whiplash, we would be honoured to render our services.

Moving is good for your back and muscles, especially if you have back pain.

Acupuncture is a centuries-old healing practice that originated in ancient China and has since gained popularity worldwide for its effectiveness in treating a wide range of health conditions. But how exactly does acupuncture work? In this article, we’ll explore the science behind acupuncture and shed light on its mechanisms of action.
Understanding Traditional Chinese Medicine
Before delving into the scientific aspects of acupuncture, it’s important to understand the principles of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) upon which it is based. According to TCM theory, the body’s vital energy, known as Qi (pronounced “chee”), flows through meridians or pathways in the body. When the flow of Qi is disrupted or blocked, illness and pain can result.
Acupuncture Points and Meridians
Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body known as acupuncture points or acupoints. These points are located along the meridians and are believed to correspond to different organs and functions in the body. By stimulating these points, acupuncturists aim to restore the balance and flow of Qi, promoting healing and well-being.
Scientific Explanations for Acupuncture
While the concepts of Qi and meridians may seem abstract to some, modern research has provided scientific explanations for the effects of acupuncture. Here are some of the key mechanisms by which acupuncture is believed to work:
1. Stimulation of Nerve Endings: Acupuncture needles stimulate nerve endings in the skin and muscles, sending signals to the brain. This can trigger the release of neurotransmitters such as endorphins and serotonin, which have pain-relieving and mood-enhancing effects.
2. Modulation of Neurotransmitters: Acupuncture has been shown to influence the levels of various neurotransmitters in the brain, including opioid peptides, which are natural painkillers produced by the body. By modulating these neurotransmitters, acupuncture can help regulate pain perception and mood.
3. Regulation of Blood Flow: Acupuncture can affect blood flow to specific areas of the body, promoting circulation and delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues. Improved blood flow can aid in the healing process and reduce inflammation and pain.
4. Activation of the Autonomic Nervous System: Acupuncture has been found to activate the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and immune response. This activation can have widespread effects on various physiological processes in the body.
5. Regulation of Neuroendocrine Pathways: Acupuncture can influence the release of hormones and other signaling molecules involved in the body’s stress response and immune function. By regulating these neuroendocrine pathways, acupuncture can help restore balance and promote health.
In conclusion, acupuncture may have ancient roots, but its efficacy is supported by modern scientific research. By stimulating specific points on the body, acupuncture can trigger a variety of physiological responses that promote healing and alleviate symptoms. Whether you’re seeking relief from pain, stress, or other health concerns, acupuncture offers a safe and effective treatment option backed by both tradition and science.
Plantar fasciitis is inflammation of the thick tissue on the bottom of the foot that connects the heel to the toes and creates the arch of the foot.
The most common complaint is pain in the bottom of the heel. The heel pain may be dull or sharp. The bottom of the foot may also ache or burn. This can be painful and make walking more difficult.
The pain is usually worse:
The pain may develop slowly over time, or suddenly after intense activity.
Plantar fasciitis develops because of repeated small tears to the flat band of ligamentous tissue that connects your heel to the bones of your toes. These tears weaken the arch that supports the foot. As the arch of the foot weakens, increasing strain is placed on the deeper ligaments and tendons of the foot and lower leg. Over time, Plantar Fasciitis can result in Chronic Pain, Heel Spurs and Degenerative Joint Disease (Arthritis).
You are more likely to get plantar fasciitis if you have:
• Foot arch problems (both flat feet and high arches)
• Long-distance running, especially running downhill or on uneven surfaces
• Sudden weight gain or obesity
• Tight Achilles tendon (the tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel)
• Shoes with poor arch support or soft soles
Plantar fasciitis is seen in both men and women. However, it most often affects active men ages 40 – 70. It is one of the most common orthopedic complaints relating to the foot.
Plantar fasciitis is commonly thought of as being caused by a heel spur, but research has found that this is not the case. On x-ray, heel spurs are seen in people with and without plantar fasciitis.
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. This may show:
• Tenderness on the bottom of your foot
• Flat feet or high arches
• Mild foot swelling or redness
• Stiffness or tightness of the arch in the bottom of your foot.
Physicians typically treat Plantar Fasciitis with anti-inflammatory drugs and steroid injections. These medications temporarily reduce the pain associated with Plantar Fasciitis but do not treat the cause of the problem. Traditional methods can usually take between 9 months to two years to resolve this condition.
Our program utilizes the latest class IV Lasers, and combines them with other therapies to help reduce the pain, strengthen the muscles around the foot and ankle joints, and increase range of motion. The Class IV Laser is at the heart of our treatment program. It provides a safe, effective, non-invasive, painless solution for plantar fasciitis. Patients generally respond exceptionally well to treatments and usually notice significant pain relief after just a few treatments.
Ending the pain caused by Plantar Fasciitis requires stopping the cycle of inflammation. This is critical because chronically inflamed tissues block the flow of needed nutrients and oxygen to surrounding muscles and joints. The advanced CLASS IV LASER restores the flow of nutrients and oxygen to the inflamed tissue allowing the cells to repair themselves at an accelerated rate.
Most cases of plantar fasciitis are resolved very easily with Class IV Laser Therapy alone; however, if the condition has become chronic this can lead to alterations in the gait that will have to be addressed. This could involve stabilizing the arch with orthotics or implementing a simple series of specific strengthening and stretching exercises.
Plantar fasciitis when treated early has an exceptionally good prognosis with our protocol. We encourage those with Plantar Fasciitis to seek our help right away. The longer one suffers with this painful condition the more likely it will cause other conditions in the knee, hip and spine.

| Ischial Bursitis |
| Ischial bursitis is the irritation of the bursa at the bony prominence behind the pelvis, called ischial tuberosity. This bony prominence represents an insertion zone for several muscles, including the hamstrings, and provides support in the sitting position. Activities and sports that require the hamstring muscles to be repeatedly contracted or stretched during running, jumping or kicking can cause irritation of the bursa and sometimes inflammation. Ischial bursitis usually results from injury to the hamstring tendons. Prolonged sitting on a hard surface or falling on the buttocks can also aggravate the irritation. ▬▬▬▬▬ Structures involved The bursa is a small fluid-filled sac. The bursa located in the pelvis acts as a lubricant to reduce friction between the muscles and the ischial tuberosity. ▬▬▬▬▬ Signs & Symptoms that you may experience Each person will react differently after an injury and recovery will depend on the severity of the injury. Ischial bursitis can produce, but is not limited to pain in the buttock area, localized swelling of the bursa and reduced mobility at the hip. ▬▬▬▬▬ Recovery Your rehabilitation plan, health profile, fitness level and nutritional status affect the recovery time. In most cases, you can expect a full recovery from ischial bursitis. As a general rule, this condition may take a few months to fully recover.1 |