Be careful out there on the roads tonight! Kids are everywhere!

Be careful out there on the roads tonight! Kids are everywhere!



Pubalgia is pain in the central point of the pubis, the pubic symphysis, which develops mainly after overexertion during sports activities. Repeated microtraumas or excessive strain on the abdominal and hip adductor muscles can cause slight shearing of this joint and generate pain felt in the groin area.
Pubalgia can produce, but is not limited to, pain in the pubic area and towards the groin area, difficulty in tolerating weight bearing and impacts during walking and running.
Relative rest is a good way to protect yourself and prevent your pubalgia from getting worse, but it’s important to avoid overprotecting. A few days of rest by reducing activities that cause pain may be needed. A progressive return to your activities of daily living, light cardiovascular activities that do not cause pain, and strengthening exercises will allow for better recovery.
#Chiropractic #PainRelief #Healthyliving #LaserTherapy #Winnipeg #BackPain #NeckPain #Headache #Fitness #Athlete #Wellness

Proper #lifting techniques are important to avoid injury and strain on the body. Whether you are lifting a heavy object at work or lifting weights at the gym, it is important to use proper lifting techniques to avoid injury and ensure that you are getting the most out of your workouts. Here are some tips for proper lifting methods:
By following these tips for proper lifting techniques, you can help to reduce the risk of injury and ensure that you are getting the most out of your workouts. Remember, if you are lifting an object that is too heavy for you to handle safely, it is important to seek assistance or use proper lifting aids. It is always better to err on the side of caution to avoid injury.

The 2014 study underscores a concerning trend among American youth, revealing that the majority fail to meet the federally recommended guideline of 60 minutes of daily physical activity. In response to this pressing public health concern, the study offers a range of actionable strategies aimed at facilitating children’s attainment of the recommended activity goals.
One proposed intervention is the implementation of mandatory daily physical education classes in schools, ensuring that children have regular opportunities to engage in structured physical activity throughout the school day. Additionally, integrating classroom-based physical activity breaks into academic curriculum can inject bursts of movement into sedentary periods, fostering an active learning environment.
Encouraging alternative modes of transportation, such as walking or biking to school, not only promotes physical activity but also reduces reliance on motor vehicles, contributing to environmental sustainability. Moreover, renovating community parks to include a diverse array of equipment and activity opportunities can transform outdoor spaces into vibrant hubs of recreational activity, enticing children to engage in active play.
The study also advocates for the expansion of after-school physical activity programs, providing children with structured opportunities for exercise and socialization beyond the school day. Furthermore, modifying school playgrounds to incorporate features that facilitate active play can empower children to engage in spontaneous physical activity during recess and leisure time.
Lead author Dr. David Bassett emphasizes the importance of leveraging these evidence-based strategies to inform policy decisions and initiatives aimed at promoting physical activity among youth. By adopting a multifaceted approach that addresses environmental, educational, and recreational factors, stakeholders can collaboratively work towards creating a culture of active living that empowers children to lead healthy, physically active lifestyles.
American Journal of Preventive Medicine, March 2015

Whiplash is an injury to the soft-tissues of the neck often referred to as a sprain or strain. Because there are a unique set of symptoms associated with whiplash, doctors and researchers commonly use the term “whiplash associated disorders” or WAD to describe the condition.
WAD commonly occurs as a result of a car crash, but it can also result from a slip and fall, sports injury, a personal injury (such as an assault), and other traumatic causes. The tissues commonly involved include muscle tendons (“strain”), ligaments and joint capsules (“sprains”), disk injuries (tears, herniation), as well as brain injury or concussion—even without hitting the head!
Symptoms vary widely but often include neck pain, stiffness, tender muscles and connective tissue (myofascial pain), headache, dizziness, sensations such as burning, prickly, tingling, numbness, muscle weakness, and referred pain to the shoulder blade, mid-back, arm, head, or face. If concussion occurs, additional symptoms include cognitive problems, concentration loss, poor memory, anxiety/depression, nervousness/irritability, sleep disturbance, fatigue, and more!
Whiplash associated disorders can be broken down into three categories: WAD I includes symptoms without any significant examination findings; WAD II includes loss of cervical range of motion and evidence of soft-tissue damage; and WAD III includes WAD II elements with neurological loss—altered motor and/or sensory functions. There is a WAD IV which includes fracture, but this is less common and often excluded.
Treatment for WAD includes everything from doing nothing to intensive management from multiple disciplines—chiropractic, primary care, physical therapy, clinical psychology, pain management, and specialty services such as neurology, orthopedics, and more. The goal of treatment is to restore normal function and activity participation, as well as symptom management.
The prognosis of WAD is generally good as many will recover without residual problems within days to weeks, with most people recovering around three months after the injury. Unfortunately, some are not so lucky and have continued neck pain, stiffness, headache, and some develop post-concussive syndrome. The latter can affect cognition, memory, vision, and other brain functions. Generally speaking, the higher the WAD category, the worse the prognosis, although each case MUST be managed by its own unique characteristics. If the injury includes neurological loss (muscle strength and/or sensory dysfunction like numbness, tingling, burning, pressure), the prognosis is often worse.
Chiropractic care for the WAD patient can include manipulation, mobilization, and home-based exercises, as well as the use of anti-inflammatory herbs (ginger, turmeric, proteolysis enzymes (bromelain, papain), devil’s claw, boswellia extract, rutin, bioflavonoid, vitamin D, coenzyme Q10, etc.) and dietary modifications aimed at reducing inflammation and promoting healing.
* 83% of those patients involved in an MVA will suffer whiplash injury and 50% will be symptomatic at 1 year.
* 90% of patients with neurologic signs at onset may be symptomatic at 1 year.
* 25- 80% of patients who suffer a whiplash injury will experience late-onset dizziness
* Clinicians should be observant for radiographic signs of instability, including interspinous widening, vertebral subluxation, vertebral compression fracture, and loss of cervical lordosis.
* Horizontal displacement of greater than 3.5 mm or angular displacement of more than 11 degrees on flexion/extension views suggests instability

Posture assessment is a key component of the chiropractic examination, and the posture of the head and neck is especially important for a patient recovering from a whiplash injury. Forward head carriage describes a state in which the head sits more forward on the shoulders than it should. In order for the muscles in the neck and shoulders to keep the head upright, they must work harder. This added strain can increase one’s risk for neck pain and headaches, which is why retraining posture is a key component to the management of neck pain and headaches in patients with or without a history of whiplash.
Forward head carriage also increases the distance between the back of the head and the headrest in the seated position, especially when the seat is reclined. In a rear-end collision, a gap greater than a half an inch between the head rest and the back of the head increases the probability of injury due to the greater distance the head can hyperextend as it rebounds backwards into the headrest. This makes posture correction of forward head carriage an important aspect of treatment from both a preventative and curative perspective.
So this begs the question, can forward head carriage be corrected? The simple answer is “yes!” One study evaluated the effects of a 16-week resistance and stretching program designed to address forward head posture and protracted shoulder positioning.
Researchers conducted the study in two separate secondary schools with 130 adolescents aged 15–17 years with forward head and protracted shoulder posture. The control group participated in a regular physical education (PE) program while the experimental group attended the same PE classes with the addition of specific exercises for posture correction. The research ream measured the teens’ shoulder head posture from the side using two different validated methods and tracked symptoms using a questionnaire. The results revealed a significant improvement in the shoulder and cervical angle in the experimental group that did not occur in the control group.
The conclusion of the study strongly supports that a 16-week resistance and stretching program is effective in decreasing forward head and protracted shoulder posture in adolescents. This would suggest that a program such as this should be strongly considered in the regular curriculum of PE courses since this is such a common problem.
Doctors of chiropractic are trained to evaluate and manage forward head posture with shoulder protraction. This can prove beneficial in both the prevention as well as management of signs and symptoms associated with a whiplash injury.

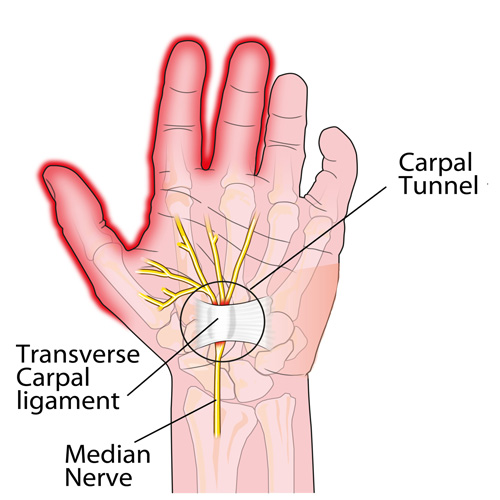
This week, we will conclude our three-part series on important facts regarding carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS).
CTS TREATMENT OPTIONS (continued): Aside from the carpal tunnel, there are several places where the median nerve can become compressed as it travels from the neck, down through the shoulder, through tight muscular areas of the upper arm and forearm, and finally through the carpal tunnel at the wrist. In order to achieve good, long-lasting results, treatment must focus on relieving compression at any point along the course of the nerve. This is why chiropractic works SO WELL as it addresses ALL of these areas using manual adjustments, muscle release techniques, and even physical therapy modalities.
CTS PREVENTION: Because there are multiple causes of CTS, prevention must be tailored to each person. For example, if the patient has diabetes mellitus, maintaining a proper blood sugar level is very important because the blood becomes thicker as the sugar levels increase and it simply cannot pass through our small blood vessels (capillaries), especially those located in the feet and hands. This can eventually lead to the need for amputation due to poor circulation and contribute to the numbness associated with diabetic neuropathy.
Similarly, low thyroid function results in a type of swelling called myxedema that can cause or worsen CTS, and keeping the thyroid hormone balanced in the bloodstream is very important. Managing other conditions that create inflammation or swelling, such as rheumatoid and other types of arthritis, will also help prevent CTS from developing or worsening.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can also occur during pregnancy due to the hormonal shifts similar for those taking birth control pills. The PRICE treatment options presented last month can be very helpful for the pregnant mother and represent important non-medication self-care approaches.
Certain occupations that require fast, repetitive work and/or firm gripping can result in carpal tunnel syndrome because of the friction that results in swelling that occurs when the muscle tendons inside the carpal tunnel rub excessively fast together (kind of like starting a fire with two sticks). Modifying the work task until the swelling is controlled is VERY important, as discussed last month.
Other preventative measures include exercises that keep the muscles and tendons in the forearm and inside the carpal tunnel stretched so that the tendons easily slide inside their respective muscle tendon sheaths. This is accomplished by placing the palm side of the hand (elbow straight) on a wall with the fingers pointing downwards while reaching across with the opposite hand and pulling the thumb back until you feel a good firm stretch. Hold this position for 5-10 seconds or until the forearm muscles feel like they are relaxing. Repeat this multiple times a day.
We realize you have a choice in whom you consider for your health care provision and we sincerely appreciate your trust in choosing our service for those needs. If you, a friend, or family member requires care for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, we would be honored to render our services.


Most likely, everyone reading this article has had a headache at one time or another. The American Headache Society reports that nearly 40% of the population suffers from episodic headaches each year while 3% have chronic tension-type headaches. The United States Department of Health and Human Services estimates that 29.5 million Americans experience migraines, but tension headaches are more common than migraines at a frequency of 5 to 1. Knowing the difference between the two is important, as the proper diagnosis can guide treatment in the right direction.
TENSION HEADACHES: These typically result in a steady ache and tightness located in the neck, particularly at the base of the skull, which can irritate the upper cervical nerve roots resulting in radiating pain and/or numbness into the head. At times, the pain can reach the eyes but often stops at the top of the head. Common triggers include stress, muscle strain, or anxiety.
MIGRAINE HEADACHES: Migraines are often much more intense, severe, and sometimes incapacitating. They usually remain on one side of the head and are associated with nausea and/or vomiting. An “aura”, or a pre-headache warning, often comes with symptoms such as a bright flashing light, ringing or noise in the ears, a visual floater, and more. For migraine headaches, there is often a strong family history, which indicates genetics may play a role in their origin.
There are many causes for headaches. Commonly, they include lack of sleep and/or stress and they can also result from a recent injury—such as a car accident, and/or a sports injury—especially when accompanied by a concussion.
Certain things can “trigger” a migraine including caffeine, chocolate, citrus fruits, cured meats, dehydration, depression, diet (skipping meals), dried fish, dried fruit, exercise (excessive), eyestrain, fatigue (extreme), food additives (nitrites, nitrates, MSG), lights (bright, flickering, glare), menstruation, some medications, noise, nuts, odors, onions, altered sleep, stress, watching TV, red wine/alcohol, weather, etc.
Posture is also a very important consideration. A forward head carriage is not only related to headaches, but also neck and back pain. We’ve previously pointed out that every inch (2.54 cm) the average 12 pound head (5.44 kg) shifts forwards adds an EXTRA ten pounds (4.5 kg) of load on the neck and upper back muscles to keep the head upright.
So, what can be done for people who suffer from headaches? First, research shows chiropractic care is highly effective for patients with both types of headaches. Spinal manipulation, deep tissue release techniques, and nutritional counseling are common approaches utilized by chiropractors. Patients are also advised to use some of these self-management strategies at home as part of their treatment plan: the use of ice, self-trigger point therapy, exercise (especially strengthening the deep neck flexors), and nutritional supplements.

Fibromyalgia (FM) is a very common, chronic condition where the patient describes “widespread pain” not limited to one area of the body. Hence, when addressing exercises for FM, one must consider the whole body. Perhaps one of the most important to consider is the squat.
If you think about it, we must squat every time we sit down, stand up, get in/out of our car, and in/out of bed. Even climbing and descending steps results in a squat-lunge type of movement.
The problem with squatting is that we frequently lose (or misuse) the proper way to do this when we’re in pain as the pain forces us to compensate, which can cause us to develop faulty movement patterns that can irritate our ankles, knees, hips, and spine (particularly the low back). In fact, performing a squatting exercise properly will strengthen the hips, which will help protect the spine, and also strengthens the glutel muscles, which can help you perform all the daily activities mentioned above.
The “BEST” type of squat is the free-standing squat. This is done by bending the ankles, knees, and hips while keeping a curve in the low back. The latter is accomplished by “…sticking the butt out” during the squat.
Do NOT allow the knees to drift beyond your toes! If you notice sounds coming from your knees they can be ignored IF they are not accompanied by pain. If you do have pain, try moving the foot of the painful knee about six inches (~15 cm) ahead of the other and don’t squat as far down. Move within “reasonable boundaries of pain” by staying away from positions that reproduce sharp, lancinating pain that lingers upon completion.