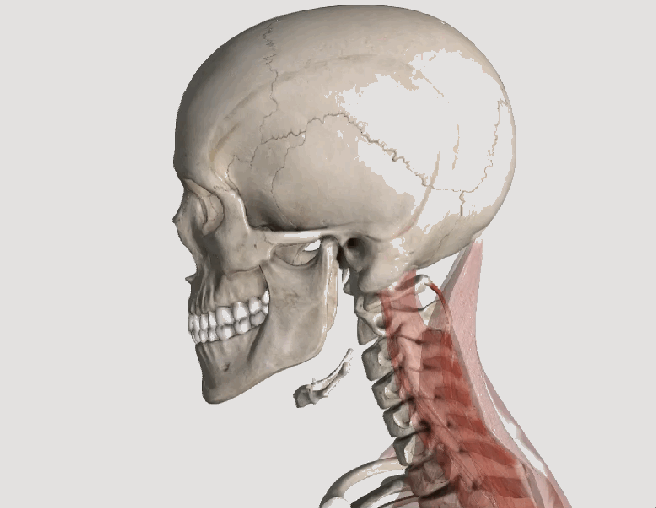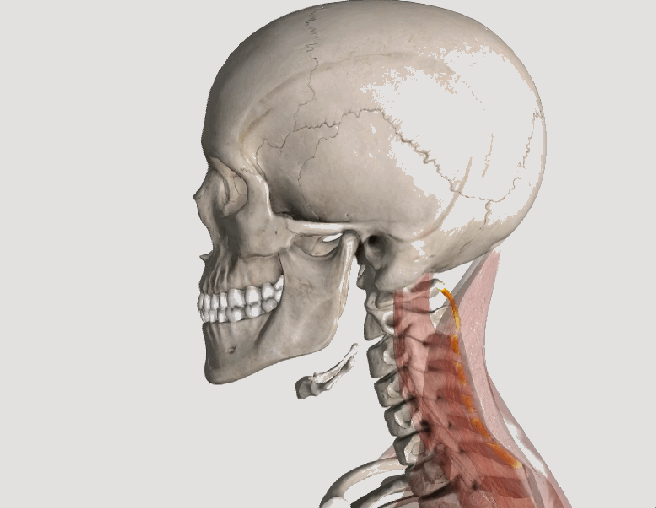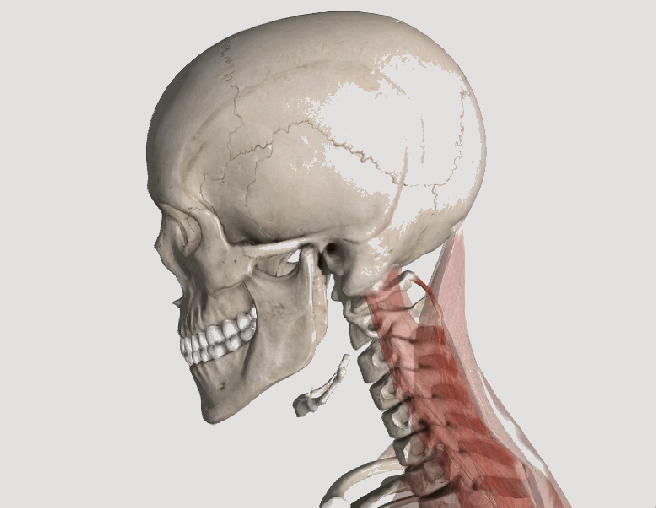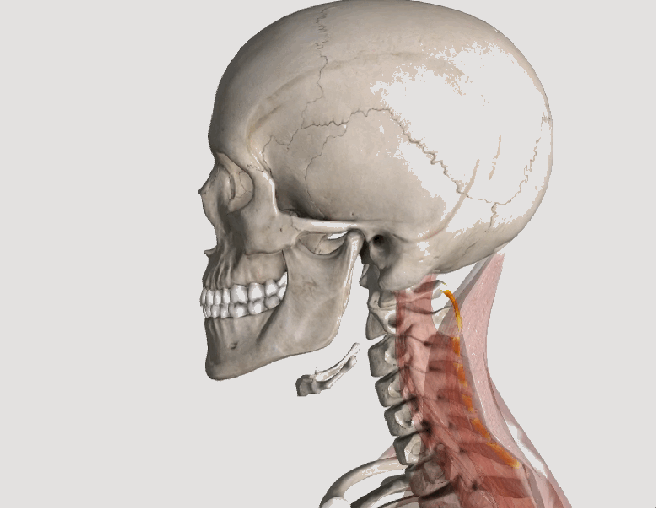
Posture assessment is a key component of the chiropractic examination, and the posture of the head and neck is especially important for a patient recovering from a whiplash injury. Forward head carriage describes a state in which the head sits more forward on the shoulders than it should. In order for the muscles in the neck and shoulders to keep the head upright, they must work harder. This added strain can increase one’s risk for neck pain and headaches, which is why retraining posture is a key component to the management of neck pain and headaches in patients with or without a history of whiplash.
Forward head carriage also increases the distance between the back of the head and the headrest in the seated position, especially when the seat is reclined. In a rear-end collision, a gap greater than a half an inch between the head rest and the back of the head increases the probability of injury due to the greater distance the head can hyperextend as it rebounds backwards into the headrest. This makes posture correction of forward head carriage an important aspect of treatment from both a preventative and curative perspective.
So this begs the question, can forward head carriage be corrected? The simple answer is “yes!” One study evaluated the effects of a 16-week resistance and stretching program designed to address forward head posture and protracted shoulder positioning.
Researchers conducted the study in two separate secondary schools with 130 adolescents aged 15–17 years with forward head and protracted shoulder posture. The control group participated in a regular physical education (PE) program while the experimental group attended the same PE classes with the addition of specific exercises for posture correction. The research ream measured the teens’ shoulder head posture from the side using two different validated methods and tracked symptoms using a questionnaire. The results revealed a significant improvement in the shoulder and cervical angle in the experimental group that did not occur in the control group.
The conclusion of the study strongly supports that a 16-week resistance and stretching program is effective in decreasing forward head and protracted shoulder posture in adolescents. This would suggest that a program such as this should be strongly considered in the regular curriculum of PE courses since this is such a common problem.
Doctors of chiropractic are trained to evaluate and manage forward head posture with shoulder protraction. This can prove beneficial in both the prevention as well as management of signs and symptoms associated with a whiplash injury.