Chronic Pain
Put the shovel down and read this!

Your low back consists of 5 individual vertebrae stacked on top of each other. Flexible cushions called “discs” live between each set of vertebrae. A disc is made up of two basic components. The inner disc, called the “nucleus”, is like a ball of jelly about the size of a marble. This jelly is held in place by the outer part of the disc called the “annulus”, which is a tough ligament that wraps around the inner nucleus much like a ribbon wrapping around your finger.
 Your low back relies on discs and other ligaments for support. “Discogenic Low Back Pain” develops when these tissues are placed under excessive stress, much like a rope that frays when it is stretched beyond its normal capacity. Most commonly, disc pain is not the result of any single event, but rather from repeated overloading. Your lumbar discs generally manage small isolated stressors quite well, but repetitive challenges lead to injury in much the same way that constantly bending a piece of copper wire will cause it to break. Examples of these stressors include: bad postures, sedentary lifestyles, poor fitting workstations, repetitive movements, improper lifting, or being overweight.
Your low back relies on discs and other ligaments for support. “Discogenic Low Back Pain” develops when these tissues are placed under excessive stress, much like a rope that frays when it is stretched beyond its normal capacity. Most commonly, disc pain is not the result of any single event, but rather from repeated overloading. Your lumbar discs generally manage small isolated stressors quite well, but repetitive challenges lead to injury in much the same way that constantly bending a piece of copper wire will cause it to break. Examples of these stressors include: bad postures, sedentary lifestyles, poor fitting workstations, repetitive movements, improper lifting, or being overweight.
Approximately one third of adults will experience pain from a lumbar disc at some point in their lifetime. The condition is more common in men. Most lumbar disc problems occur at one of the two lowest discs- L5 or L4. Smokers and people who are generally inactive have a higher risk of lumbar disc problems. Certain occupations may place you at a greater risk, especially if you spend extended periods of time sitting or driving. People who are tall or overweight have increased risk of disc problems.
Symptoms from disc pain may begin abruptly but more commonly develop gradually. Symptoms may range from dull discomfort to surprisingly debilitating pain that becomes sharper when you move. Rest may relieve your symptoms but often leads to stiffness. The pain is generally centered in your lower back but can spread towards your hips or thighs. Be sure to tell your doctor if your pain extends beyond your knee, or if you have weakness in your lower extremities or a fever.
Repeated injuries cause your normal healthy elastic tissue to be replaced with less elastic “scar tissue.” Over time, discs may dehydrate and thin. This process can lead to ongoing pain and even arthritis. Patients who elect to forego treatment and “just deal with it” develop chronic low back pain more than 60% of the time. Seeking early and appropriate treatment like the type provided in our office is critical.
Depending on the severity of your injury, you may need to limit your activity for a while, especially bending, twisting, and lifting, or movements that cause pain. Bed rest is not in your best interest. You should remain active and return to normal activities as your symptoms allow. Light aerobic exercise (i.e. walking, swimming, etc) has been shown to help back pain sufferers. The short-term use of a lumbar support belt may be helpful. Sitting makes your back temporarily more vulnerable to sprains and strains from sudden or unexpected movements. Be sure to take “micro breaks” from workstations for 10 seconds every 20 minutes.
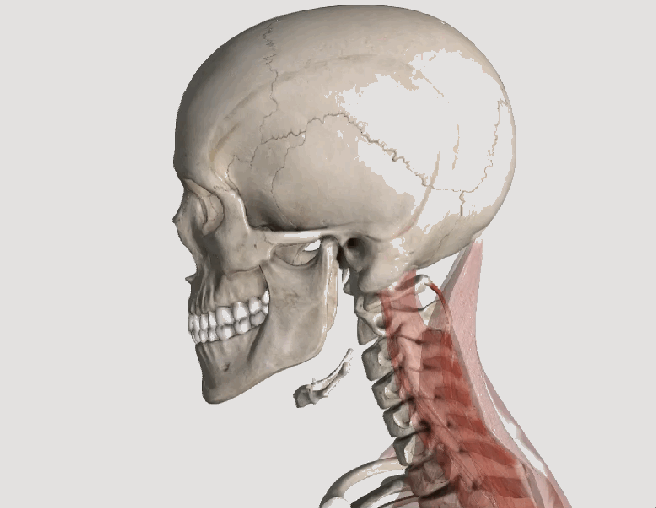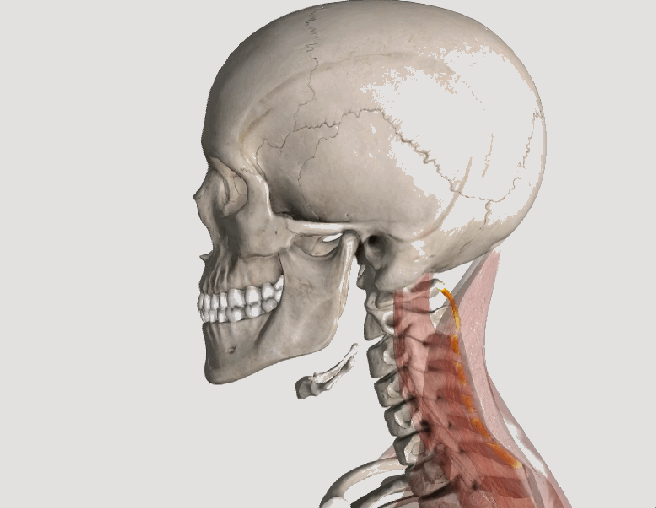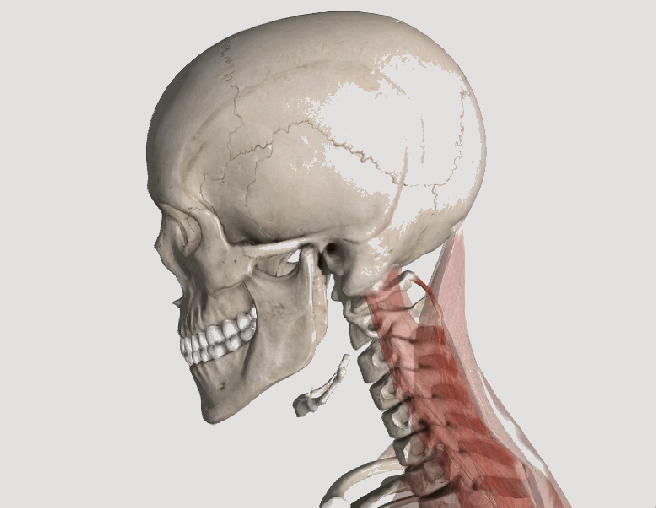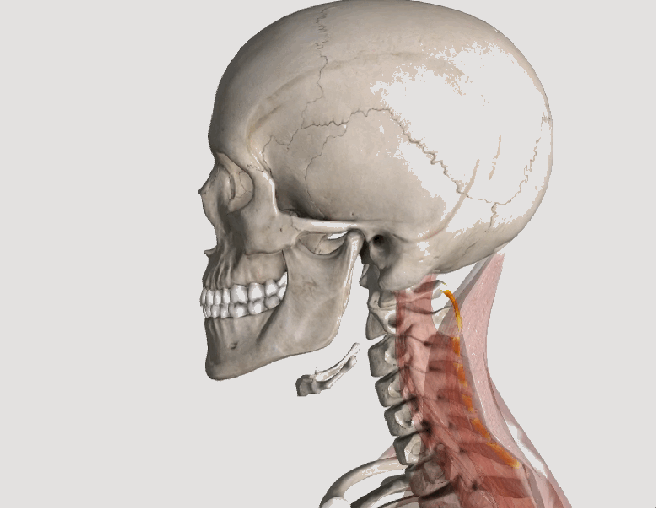
Whiplash and Your Posture

Posture assessment is a key component of the chiropractic examination, and the posture of the head and neck is especially important for a patient recovering from a whiplash injury. Forward head carriage describes a state in which the head sits more forward on the shoulders than it should. In order for the muscles in the neck and shoulders to keep the head upright, they must work harder. This added strain can increase one’s risk for neck pain and headaches, which is why retraining posture is a key component to the management of neck pain and headaches in patients with or without a history of whiplash.
Forward head carriage also increases the distance between the back of the head and the headrest in the seated position, especially when the seat is reclined. In a rear-end collision, a gap greater than a half an inch between the head rest and the back of the head increases the probability of injury due to the greater distance the head can hyperextend as it rebounds backwards into the headrest. This makes posture correction of forward head carriage an important aspect of treatment from both a preventative and curative perspective.
So this begs the question, can forward head carriage be corrected? The simple answer is “yes!” One study evaluated the effects of a 16-week resistance and stretching program designed to address forward head posture and protracted shoulder positioning.
Researchers conducted the study in two separate secondary schools with 130 adolescents aged 15–17 years with forward head and protracted shoulder posture. The control group participated in a regular physical education (PE) program while the experimental group attended the same PE classes with the addition of specific exercises for posture correction. The research ream measured the teens’ shoulder head posture from the side using two different validated methods and tracked symptoms using a questionnaire. The results revealed a significant improvement in the shoulder and cervical angle in the experimental group that did not occur in the control group.
The conclusion of the study strongly supports that a 16-week resistance and stretching program is effective in decreasing forward head and protracted shoulder posture in adolescents. This would suggest that a program such as this should be strongly considered in the regular curriculum of PE courses since this is such a common problem.
Doctors of chiropractic are trained to evaluate and manage forward head posture with shoulder protraction. This can prove beneficial in both the prevention as well as management of signs and symptoms associated with a whiplash injury.
What Causes Low Back Pain?
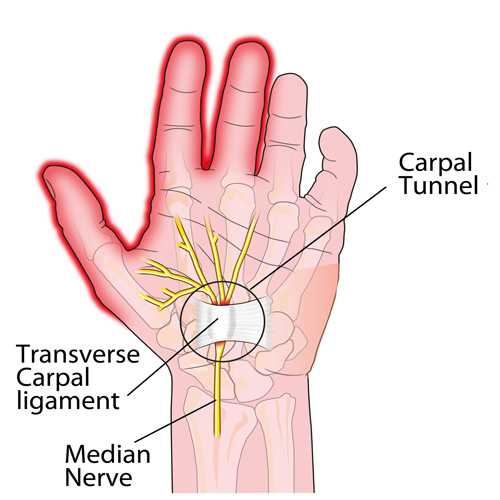
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome #3

This week, we will conclude our three-part series on important facts regarding carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS).
CTS TREATMENT OPTIONS (continued): Aside from the carpal tunnel, there are several places where the median nerve can become compressed as it travels from the neck, down through the shoulder, through tight muscular areas of the upper arm and forearm, and finally through the carpal tunnel at the wrist. In order to achieve good, long-lasting results, treatment must focus on relieving compression at any point along the course of the nerve. This is why chiropractic works SO WELL as it addresses ALL of these areas using manual adjustments, muscle release techniques, and even physical therapy modalities.
CTS PREVENTION: Because there are multiple causes of CTS, prevention must be tailored to each person. For example, if the patient has diabetes mellitus, maintaining a proper blood sugar level is very important because the blood becomes thicker as the sugar levels increase and it simply cannot pass through our small blood vessels (capillaries), especially those located in the feet and hands. This can eventually lead to the need for amputation due to poor circulation and contribute to the numbness associated with diabetic neuropathy.
Similarly, low thyroid function results in a type of swelling called myxedema that can cause or worsen CTS, and keeping the thyroid hormone balanced in the bloodstream is very important. Managing other conditions that create inflammation or swelling, such as rheumatoid and other types of arthritis, will also help prevent CTS from developing or worsening.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can also occur during pregnancy due to the hormonal shifts similar for those taking birth control pills. The PRICE treatment options presented last month can be very helpful for the pregnant mother and represent important non-medication self-care approaches.
Certain occupations that require fast, repetitive work and/or firm gripping can result in carpal tunnel syndrome because of the friction that results in swelling that occurs when the muscle tendons inside the carpal tunnel rub excessively fast together (kind of like starting a fire with two sticks). Modifying the work task until the swelling is controlled is VERY important, as discussed last month.
Other preventative measures include exercises that keep the muscles and tendons in the forearm and inside the carpal tunnel stretched so that the tendons easily slide inside their respective muscle tendon sheaths. This is accomplished by placing the palm side of the hand (elbow straight) on a wall with the fingers pointing downwards while reaching across with the opposite hand and pulling the thumb back until you feel a good firm stretch. Hold this position for 5-10 seconds or until the forearm muscles feel like they are relaxing. Repeat this multiple times a day.
We realize you have a choice in whom you consider for your health care provision and we sincerely appreciate your trust in choosing our service for those needs. If you, a friend, or family member requires care for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, we would be honored to render our services.
Do I have a tension headache? Or Migranes?


Most likely, everyone reading this article has had a headache at one time or another. The American Headache Society reports that nearly 40% of the population suffers from episodic headaches each year while 3% have chronic tension-type headaches. The United States Department of Health and Human Services estimates that 29.5 million Americans experience migraines, but tension headaches are more common than migraines at a frequency of 5 to 1. Knowing the difference between the two is important, as the proper diagnosis can guide treatment in the right direction.
TENSION HEADACHES: These typically result in a steady ache and tightness located in the neck, particularly at the base of the skull, which can irritate the upper cervical nerve roots resulting in radiating pain and/or numbness into the head. At times, the pain can reach the eyes but often stops at the top of the head. Common triggers include stress, muscle strain, or anxiety.
MIGRAINE HEADACHES: Migraines are often much more intense, severe, and sometimes incapacitating. They usually remain on one side of the head and are associated with nausea and/or vomiting. An “aura”, or a pre-headache warning, often comes with symptoms such as a bright flashing light, ringing or noise in the ears, a visual floater, and more. For migraine headaches, there is often a strong family history, which indicates genetics may play a role in their origin.
There are many causes for headaches. Commonly, they include lack of sleep and/or stress and they can also result from a recent injury—such as a car accident, and/or a sports injury—especially when accompanied by a concussion.
Certain things can “trigger” a migraine including caffeine, chocolate, citrus fruits, cured meats, dehydration, depression, diet (skipping meals), dried fish, dried fruit, exercise (excessive), eyestrain, fatigue (extreme), food additives (nitrites, nitrates, MSG), lights (bright, flickering, glare), menstruation, some medications, noise, nuts, odors, onions, altered sleep, stress, watching TV, red wine/alcohol, weather, etc.
Posture is also a very important consideration. A forward head carriage is not only related to headaches, but also neck and back pain. We’ve previously pointed out that every inch (2.54 cm) the average 12 pound head (5.44 kg) shifts forwards adds an EXTRA ten pounds (4.5 kg) of load on the neck and upper back muscles to keep the head upright.
So, what can be done for people who suffer from headaches? First, research shows chiropractic care is highly effective for patients with both types of headaches. Spinal manipulation, deep tissue release techniques, and nutritional counseling are common approaches utilized by chiropractors. Patients are also advised to use some of these self-management strategies at home as part of their treatment plan: the use of ice, self-trigger point therapy, exercise (especially strengthening the deep neck flexors), and nutritional supplements.
What Exercises Should I Do For Fibro?

Fibromyalgia (FM) is a very common, chronic condition where the patient describes “widespread pain” not limited to one area of the body. Hence, when addressing exercises for FM, one must consider the whole body. Perhaps one of the most important to consider is the squat.
If you think about it, we must squat every time we sit down, stand up, get in/out of our car, and in/out of bed. Even climbing and descending steps results in a squat-lunge type of movement.
The problem with squatting is that we frequently lose (or misuse) the proper way to do this when we’re in pain as the pain forces us to compensate, which can cause us to develop faulty movement patterns that can irritate our ankles, knees, hips, and spine (particularly the low back). In fact, performing a squatting exercise properly will strengthen the hips, which will help protect the spine, and also strengthens the glutel muscles, which can help you perform all the daily activities mentioned above.
The “BEST” type of squat is the free-standing squat. This is done by bending the ankles, knees, and hips while keeping a curve in the low back. The latter is accomplished by “…sticking the butt out” during the squat.
Do NOT allow the knees to drift beyond your toes! If you notice sounds coming from your knees they can be ignored IF they are not accompanied by pain. If you do have pain, try moving the foot of the painful knee about six inches (~15 cm) ahead of the other and don’t squat as far down. Move within “reasonable boundaries of pain” by staying away from positions that reproduce sharp, lancinating pain that lingers upon completion.
The Best Diet For Fibromyalgia?

Fibromyalgia (FM) and its cause remains a mystery, but most studies suggest that FM is NOT the result of a single event but rather a combination of many physical, chemical, and emotional stressors.
The question of the month regarding the BEST FM diet is intriguing since one might assume that the many causes should mean that there isn’t one dietary solution. But is that true? Could there be a “best diet” to help ease the symptoms from such a multi-faceted disorder?
Certainly, healthy eating is VERY important for ALL of us regardless of our current ailment(s). Obesity is rampant largely due to the fact that 60% of the calories consumed by the “typical” American center around eating highly inflaming food that include those rich in Sugar, Omega-6 oil, Flour, and Trans fats (“SOFT” foods, if you will!). Obesity has been cited as “an epidemic” largely due to kids and adults becoming too sedentary (watching TV, playing on electronic devices, etc.) and eating poorly.
Perhaps the BEST way to manage the pain associated with FM and to maintain a healthy BMI (Body Mass Index, or ratio between height and weight) is to substitute ANTI-INFLAMING foods for those that inflame (or SOFT foods).
You can simplify your diet by substituting OUT “fast foods” for fruits, vegetables, and lean meats. So there you have it. It’s that simple. The problem is making up your mind to change and then actually doing it. Once these two things take place, most everyone can easily “recalibrate” their caloric intake and easily adapt.
Not only have studies shown that chronic illnesses like heart disease, stroke, and diabetes significantly benefit by following this simple dietary shift, but so does pain arising from the musculoskeletal system! This is because the human body is made up largely of chemicals, and chemical shifts are constantly taking place when it moves. If you reach for an anti-inflammatory drug like ibuprofen or naproxen and it helps, it’s because you ARE inflamed and the drug reduces the pain associated with that inflammation. This is an indication that an anti-inflammatory diet WILL HELP as well (but without the negative side effects)!
The list of chronic conditions that result in muscle pain not only includes FM but also obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type II diabetes. Conditions like tension-type and migraine headaches, neck and back pain, disk herniation, and tendonopathies and MANY more ALL respond WELL to making this SIMPLE change in the diet. For more information on how to “DEFLAME,” visit http://www.deflame.com! It could be a potential “lifesaver!”
I get dizzy when I have a headache. Should I worry?
Dizziness, neck pain, and headaches are very common symptoms that may or may not occur at the same time. Though this interrelationship exists, this month’s article will focus primarily on dizziness, particularly related to dizziness that occurs after standing.
First, it is important to point out that it is VERY common to be light headed or dizzy when standing up too fast, which is typically referred to as orthostatic hypotension (OH). OH is frequently referred to as a benign symptom, but new information may challenge this thought.
Let’s review what happens. When we are lying down, our heart does not have to work as hard as when we are upright; therefore, our blood pressure (BP) is usually lower while we lay in bed. When standing up, blood initially pools in the legs until an increase in blood pressure brings oxygen to the brain. This either resolves or prevents dizziness.
Orthostatic hypotension is defined as a blood pressure drop of >20 mm Hg systolic (the upper number—heart at FULL contraction), 10 mm Hg diastolic (lower number—heart at FULL rest), or both. This typically occurs within seconds to a few minutes after rising to a standing position.
There are two types of OH—delayed OH (DOH) where the onset of symptoms are not immediate but occur within three minutes of standing and “full” OH, which is more serious and occurs immediately upon rising. According to a 2016 study published in the prestigious journal Neurology, researchers reviewed the medical records of 165 people who had undergone autonomic nervous system testing for dizziness. The subjects averaged 59 years of age, and 48 were diagnosed with DOH, 42 with full OH, and 75 subjects didn’t have either condition.
During a ten-year follow-up, 54% of the DOH group progressed to OH, of which 31% developed a degenerative brain condition such as Parkinson’s disease or dementia. Those with initial DOH who also had diabetes were more likely to develop full OH vs. those without diabetes.
The early death rate in this 165 patient group was 29% for those with DOH, 64% with full OH, vs. 9% for those with neither diagnosed condition. The authors point out that those initially diagnosed with DOH who did NOT progress into full OH were given treatment that may have improved their blood pressure.
The authors state that a premature death might be avoided by having DOH and OH diagnosed and properly managed as early as possible. They point out that a prospective study is needed since this study only looked back at medical records of subjects who had nervous system testing performed at a specialized center, and therefore, these findings may not apply to the general population.
The value of this study is that this is the FIRST time a study described OH (or DOH) as a potentially serious condition with recommendations NOT to take OH/DOH lightly or view it as a benign condition. Since doctors see this a lot, a closer evaluation of the patient is in order.
Teens & Headaches? What?

In 2016, researchers at Curtin University in Perth examined the seated posture and health data of 1,108 17-year olds in an effort to determine if any particular posture increased the risk of headaches/neck pain among late adolescents.
Among four posture subgroups—upright, intermediate, slumped thorax, and forward head—the researchers observed the following: participants who were slumped in their thoracic spine (mid-back region) and had their head forward when they sat were at higher odds of having mild, moderate, or severe depression; participants classified as having a more upright posture exercised more frequently, females were more likely to sit more upright than males; those who were overweight were more likely to sit with a forward neck posture; and taller people were more likely to sit upright.
While they found biopsychosocial factors like exercise frequency, depression, and body mass index (BMI) ARE associated with headaches and neck pain, their data did not suggest any one particular posture increased the risk of neck pain or headaches more than any other posture among the teenagers involved in the study.
This is noteworthy as studies with adults do indicate the risk for neck pain and headaches is greater in individuals with poor neck posture. In particular, postures such as forward head carriage, pinching a phone between the ear and shoulder, and prolonged neck/head rotation outside of neutral can all increase the risk of cervical disorders. This suggests that in younger bodies, the cause of neck pain and headaches may be multifactoral and not limited to just poor posture and that treatment must address all issues that may increase one’s risk for neck pain/headaches in order to reach a desired outcome.
The good news is that chiropractic has long embraced the biopsychosocial model of healthcare, looking at ALL factors that affect back and neck pain and quality of life. Through patient education, spinal manipulation, mobilization, exercise training, the use of modalities, and more, chiropractors can greatly help those struggling with neck pain and headaches!